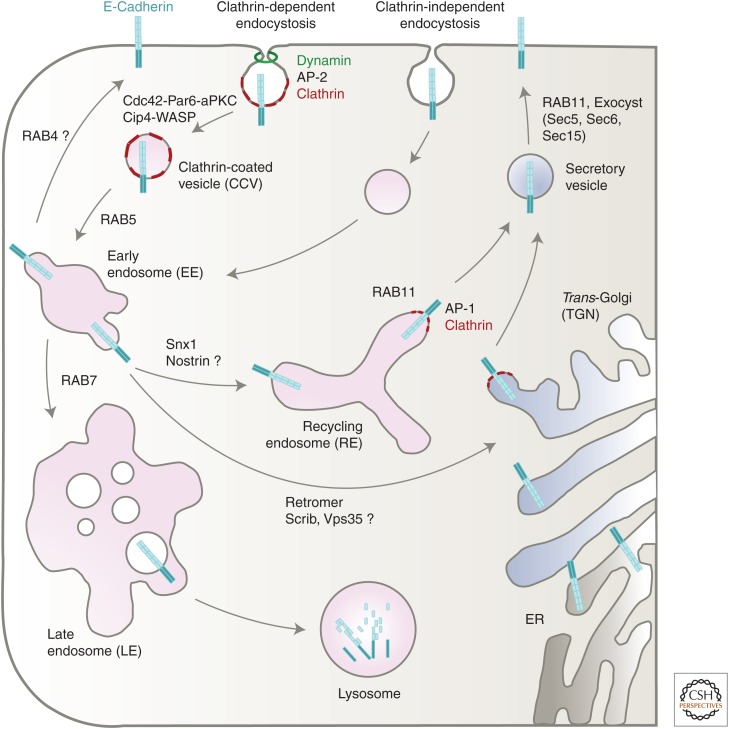
Figure 3.
Trafficking pathways of E-cadherin. E-cadherin can undergo either clathrin-dependent or independent endocytosis. Internalized E-cadherin traffic through different endosomal compartments. Numerous molecules and endocytic machineries determine the fate of E-cadherin either to endosomal recycling back to the plasma membrane or to lysosomal degradation. Polarized sorting in both the biosynthetic pathway from the trans-Golgi network and recycling endosomes requires vesicle carriers such as AP-1 as discussed in the main text.