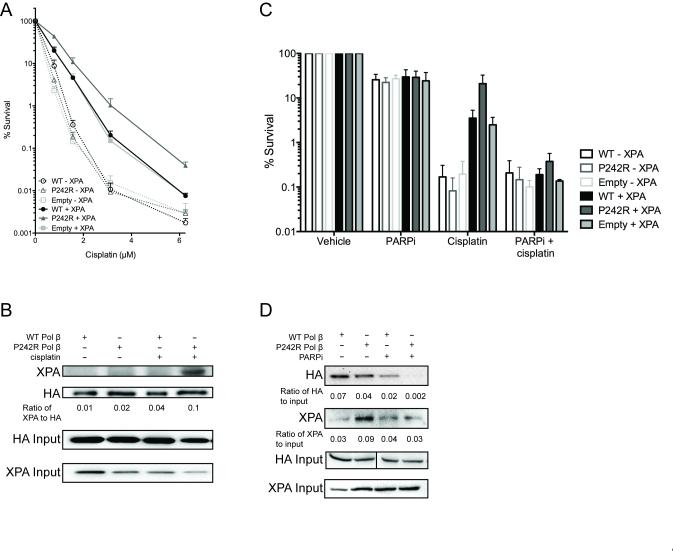
Figure 2. NER is required for P242R-mediated cisplatin resistance.
A. XP20S cells deficient in XPA (−XPA; dashed lines, open symbols) or complemented with XPA (+XPA; solid lines, filled symbols) expressing WT, P242R, or empty vector were treated with various concentrations of cisplatin (0-6.25 μM). Clonogenic survival assays were performed and data are presented as mean ± SEM of the percent survival (n = 3). B. Whole cell extracts from A549 cells expressing either HA-tagged WT or P242R Pol β were immunoprecipated with anti-HA antibody as described in Experimental Procedures. Samples were separated by SDS-PAGE and the membrane was probed with antibodies against XPA or HA. The ratio of XPA to HA was quantified and shown under the blot. Co-immunoprecipitations were performed 3 times. C. XP20S deficient in XPA (−XPA; open bars) or complemented with XPA (+XPA; solid bars) expressing WT, P242R, or empty vector were treated with 1.6 μM cisplatin in the presence or absence of 10 μM PARPi (olaparib; AZD2281). Clonogenic survival assays were performed and data are presented as mean ± SEM of the percent survival (n = 3). D. A whole cell extract binding assay was performed with biotinylated Pt-GG DNA and lysates from A549 cells expressing either HA-tagged WT or P242R Pol β as described in Experimental Procedures. Westerns were performed and membranes were probed with anti-HA or anti-XPA antibodies. The ratios of HA or XPA to 10% HA input were quantified and are shown under the blots (n=3). XPA input is also shown.