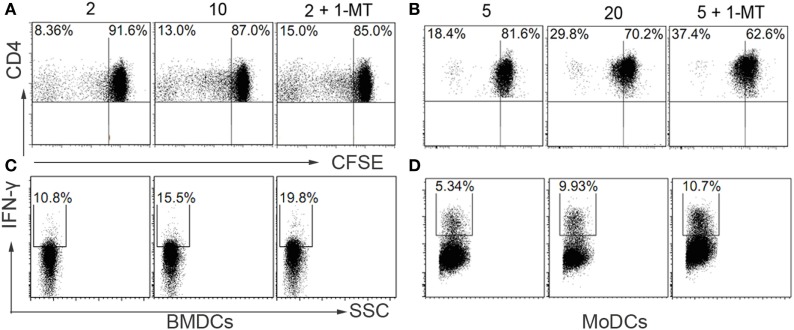
Figure 4.
Interleukin (IL)-4 affects the capability of dendritic cells (DCs) in T cell activation through regulating indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) activity. Bone marrow-derived DCs (BMDCs) and monocyte-derived DCs (MoDCs) were generated under various concentration of IL-4 (nanograms per milliliter). Then the BMDCs and MoDCs were cocultured with CFSE-labeled naïve CD4+ T cells from normal C57/BL6 mice or healthy volunteers, respectively, with or without the presence of IDO inhibitor (25 μM). After 5 days, the cells were harvested and analyzed by flow cytometry. (A,B) The CD4+ T cells proliferation was evaluated by cell division. Results are represented as mean ± SD. (C,D) The CD4+ T cells were also collected and analyzed for type 1 cytokines IFN-γ expression by flow cytometry. Results are represented as mean ± SD. The data shown are representative one of the three separate experiments.