Figure 1.
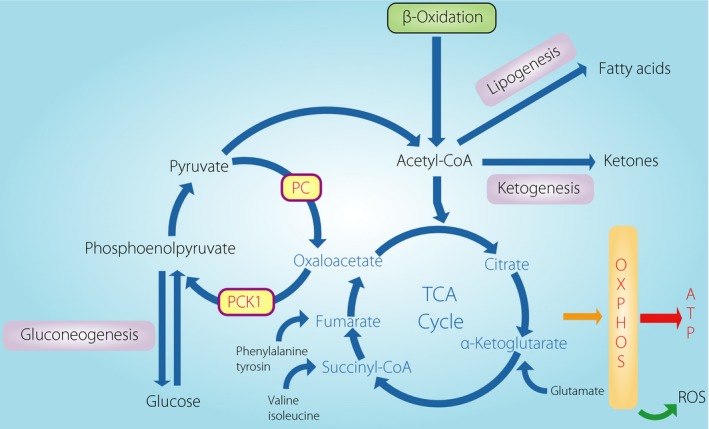
Schematic of the hepatic tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle with the major anaplerotic and cataplerotic pathways associated with glucogenonesis, lipogenesis, and ketogeneis. An elevation of fatty acid delivery amplifies the TCA cycle flux with a rise in anaplerosis/cataplerosis, leading to a proportional rise in oxidative stress and inflammation in liver. The redox state and intermetabolites in the TCA cycle amplify or suppress the flux. Oxidative stress is causal for further mitochondrial dysfunction. ATP, adenosine triphosphate; OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation; PC, pyruvate carboxylase; PCK1, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
