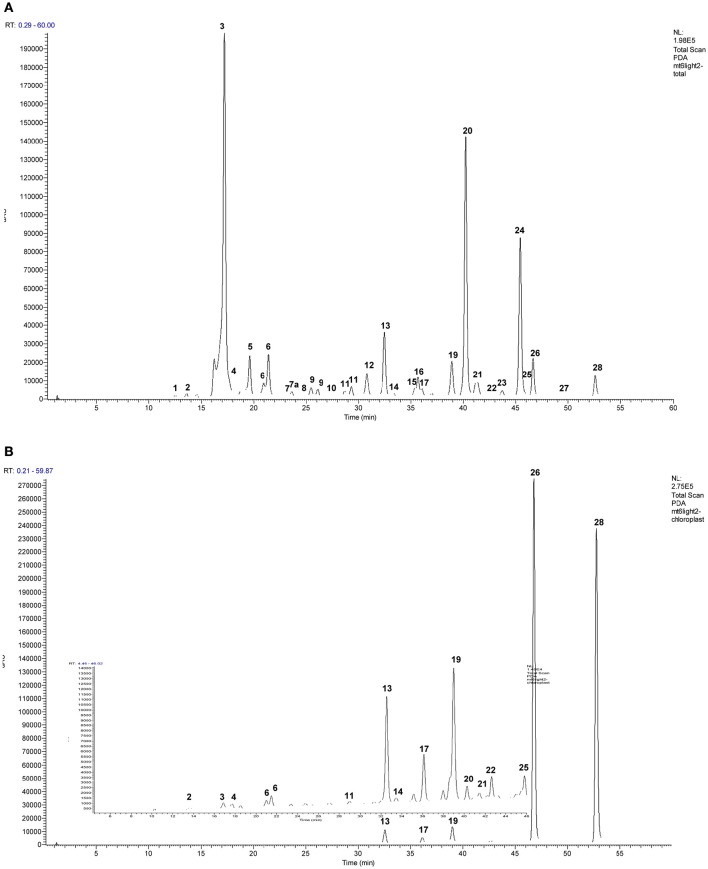
Figure 5.
Representative HPLC/UV chromatograms (240–400 nm) of the phenolics in representative purified (A) whole leaf extracts and b) chloroplasts of red clover. Final concentration of the extracts shown was 0.1 μg total chlorophyll (Chla + Chlb) μL−1 extract of which 10 μL was injected. Panel (B) has an enlarged insert to show smaller peaks more clearly. Table 4 shows detail of identified peaks 1–28: 1, caffeic acid; 2, 2-hydroxy-2,3-dihydrogenistein hexoside; 3, caffeoyl malate (phaselic acid); 4, unidentified compound; 5, caffeoyl DOPA (clovamide); 6, coumaroyl malate; 7, coumaroyl DOPA; 7a caffeoyl tyrosine; 8, feruloyl DOPA; 9, caffeoyl mevalonate (tentative); 10, coumaroyl tyrosine; 11, quercetin hexoside; 12, quercetin hexoside malonate; 13, formononetin hexoside, formic acid adduct; 14, kaempferol hexoside; 15, kaempferol hexoside malonate; 16, formononetin hexoside, sodium formate adduct; 17, irilone hexoside, formic adduct; 18, irilone conjugate formic adduct; 19, biochanin A hexoside, formic adduct; 20, formononetin hexoside malonate; 21, isomer of peak (19), formic acid adduct; 22, pratensein; 23, formononetin hexoside succinate; 24, biochanin A, hexoside malonate; 25, pseudobaptigenin; 26, formononetin; 27, biochanin A conjugate; 28, biochanin A.