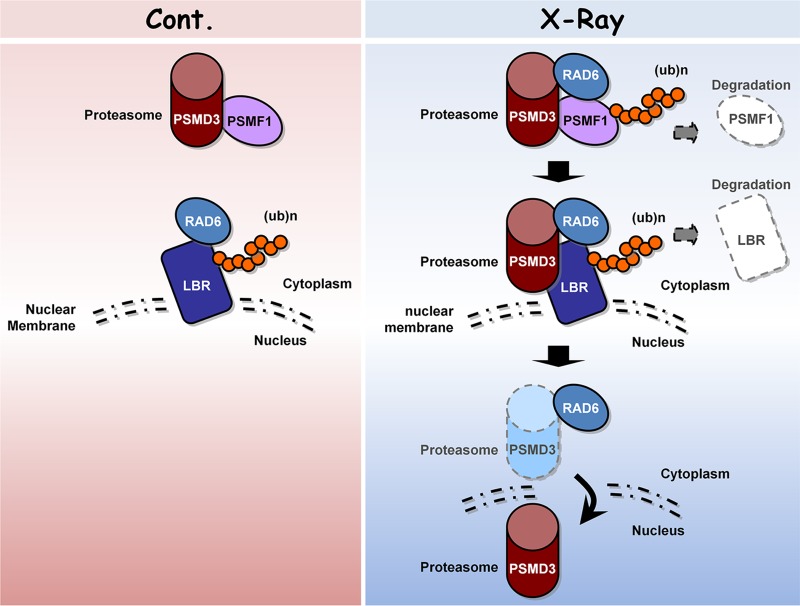
FIG 7.
Working model. Under normal conditions, proteasomes are primarily localized in the cytoplasm and proteasome activities are inhibited by the inhibitory protein PSMF1. However, when cells encounter DNA damage stress, such as X-ray irradiation, the proteasome activity is enhanced and more proteasomes enter the nucleus. The proteasome activity is regulated by RAD6 through controlling the ubiquitination and degradation of PSMF1, while the nuclear translocation of proteasomes is also regulated by RAD6 via the control of LBR ubiquitination and degradation. When cells are exposed to X-ray irradiation, the degradation of PSMF1 and LBR by RAD6 is enhanced, further increasing proteasome activity and nuclear localization.