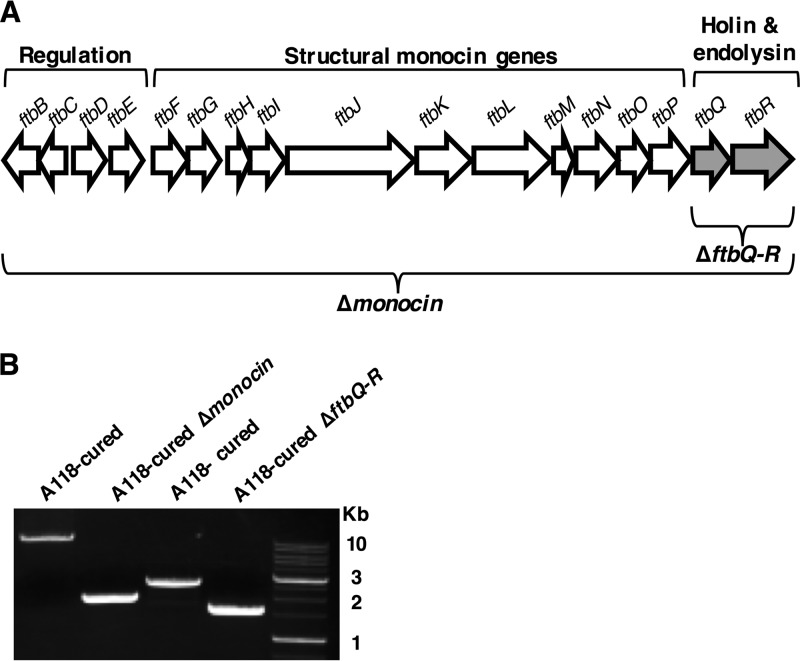
FIG 3.
Construction and validation of the Δmonocin and ΔftbQR mutants using pLR16-pheS*. (A) Schematic representation of the monocin gene region. The region is ~10.7 kbp long and consists of 17 genes (LMRG_2362 to LMRG_2378, here presented as ftbB to -R). Deletion of the whole region is designated Δmonocin, and deletion of the 1,132-bp long LMRG_2377 and LMRG_2378, encoding the holin and endolysin (marked in gray), is designated ΔftbQR. Annotation of gene groups is marked above the diagram; above the arrows, representing genes, are the gene names as designated by Lee et al. (21). (B) PCR verification of the deletion mutants. For the Δmonocin mutant, primers 15 and 18 (Table 1) were used, expecting ∼12,700-bp- and ∼2,000-bp-long products from A118 phage-cured L. monocytogenes and the Δmonocin mutant, respectively. For ΔftbQR, primers 19 and 22 (Table 1) were used, expecting ∼2,700-bp- and ∼1,600-bp-long products from A118-phage cured L. monocytogenes and ΔftbQR mutant, respectively. A 1-kb DNA ladder (GeneDireX) is shown on the right.