Figure 1.
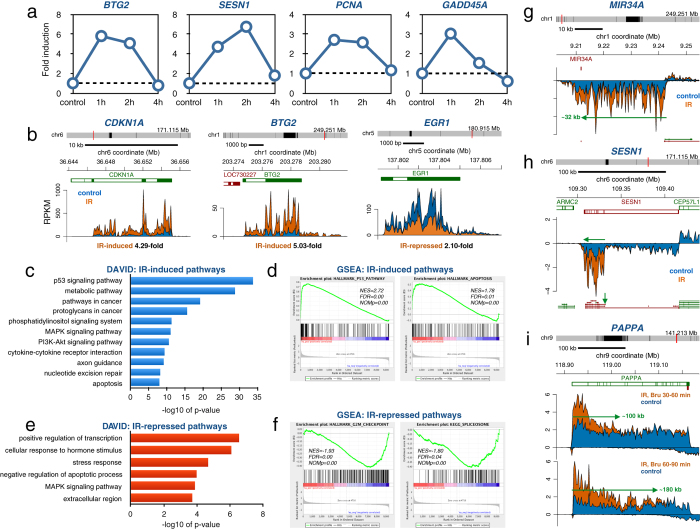
IR-induce changes in transcription in human fibroblasts (a) Human HF1 fibroblasts cells were mock-irradiated (0 h) or irradiated with 2 Gy and labeled for 60 min with 2 mM Bru either 1, 2 or 4 hours after irradiation. Bru-labeled RNA was immuno-captured and subjected to RT-PCR using the human DNA damage-response RT-PCR array. Time-course data is shown for BTG2, SESN1, PCNA and GADD45A transiently induced by IR. (b) Bru-seq data for CDKN1A, BTG2 and EGR1 from HF1 fibroblast cells either mock-irradiated (blue) or exposed to 2 Gy and labeled with 2 mM Bru for 30 min after a 1-hour post-incubation (orange). (c) DAVID functional annotation analysis of 250 genes showing significantly induced transcription following exposure to 2 Gy of IR in HF1 cells according to DESeq (n = 2). (d) Display of the highly IR-induced “p53 pathway” and “apoptosis” according to GSEA analysis listing the normalized enrichment score (NES), false discovery rate q-value (FDR) and the nominal p-value (NOMp). (e) DAVID functional annotation analysis of 33 genes showing significantly suppressed transcription following exposure to 2 Gy of IR in HF1 cells according to DESeq (n = 2). (f) Display of the highly IR-suppressed “G2/M checkpoint” and “spliceosome” according to GSEA analysis. (g) Induction of a 32 kb primary transcript of the miR34A gene 1 h after exposure of HF1 fibroblasts to 2 Gy. (h) IR-specific induction of transcription from the promoter of the short isoform but not the promoter of the long isoform of SESN1. (i) Delayed completion of IR-induced transcription of the >200 kb long PAPPA gene. The front of the IR-induced transcription wave had reached ~100 kb within 60 minutes and ~180 kb within 90 min after irradiation.