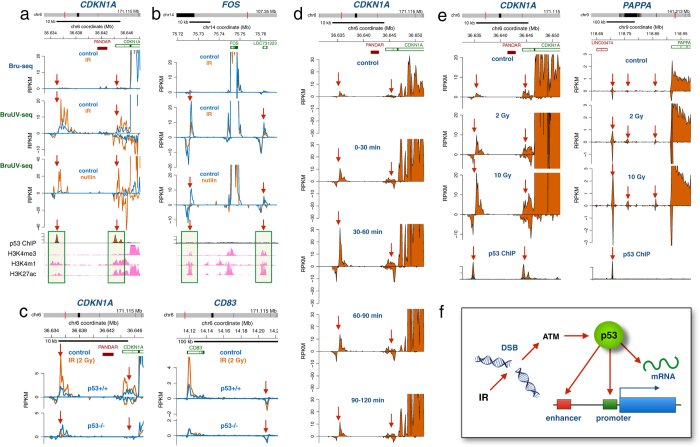
Figure 5. IR-induced activation and repression of enhancer elements mediated by p53.
(a) Human HF1 fibroblasts were irradiated with 2 Gy followed by Bru-seq or BruUV-seq after 1 hour of post-IR incubation at 37 °C. Two regions upstream of the CDKN1A gene showed strong enhancement in reads following IR when using the BruUV-seq assay (middle panel), but not when using the Bru-seq assay (top panel). These BruUV-seq peaks also showed strong enhancement in reads following a 6-hour Nutlin-3 treatment (bottom panel). The IR- and Nutlin-3-induced BruUV-seq peaks aligned closely with p53 ChIP-seq binding data (from ref. 35) and histone modifications associated with enhancer elements such as high H3K4me1, high H3K27ac and low H3K4me3 (ENCODE data from UCSC browser) (b) IR-induced suppression of BruUV-seq peaks (middle panel) were also suppressed by a 6-hour Nutlin-3 treatment (bottom panel). These peaks were not associated with p53 binding peaks but showed histone modifications affirmative of enhancer elements. (c) The IR-induced BruUV-seq peaks upstream of the CDKN1A gene (left top panel) and a peak downstream of the CD83 gene (right top panels) found in p53+/+ HCT116 cells were abolished in HCT116 cells lacking p53 (bottom panels). (d) BruUV-seq analyses were performed on HF1 human fibroblasts at different times after irradiation with 2 Gy and show a transient IR-mediated induction of nascent eRNA generated from the two putative enhancer elements upstream of the CDKN1A gene with a maximum of expression 30–60 minutes after irradiation. (e) IR induces eRNA associated with the CDKN1A and PAPPA genes in a dose-dependent manner in human HF1 cells. (f) Model of the roles of p53 in regulating the transcriptional and post-transcriptional responses following IR.