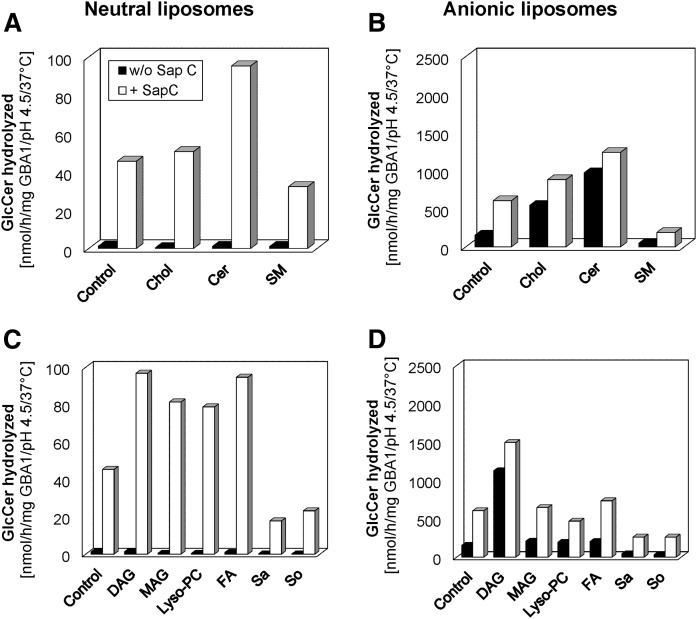
Fig. 8.
Stimulatory and inhibitory roles of various lysosomal lipid degradation products on Sap C-induced hydrolysis of membrane bound GlcCer by GBA1. GlcCer hydrolysis is insignificant in the absence of both Sap C and BMP. Sap C-induced GlcCer hydrolysis by GBA1 is enhanced strongly by Cer and slightly by cholesterol (Chol), but inhibited by SM in neutral liposomes (A) and in the presence of BMP (B), respectively. Also, the Sap C-induced GlcCer hydrolysis by GBA1 is strongly enhanced by DAG, MAG, stearic acid, and lyso-PC, but strongly inhibited by sphingosine (So) and sphinganine (Sa) in neutral liposomes (C). In the presence of BMP (D), it is enhanced strongly by DAG and slightly by MAG and stearic acid, but strongly inhibited by sphingosine and sphinganine. The effects of lyso-PC depend on the liposome types. The experiments were carried out using 10 mol% each of the stimulating or inhibiting lipids and 400 or 60 ng GBA1 per assay with 1 or 0.5 μg Sap C for neutral and BMP-containing liposomes, respectively, under 30 min incubation and at 37°C. SEM was less than 10% (n = 4–6).