Fig. 5.
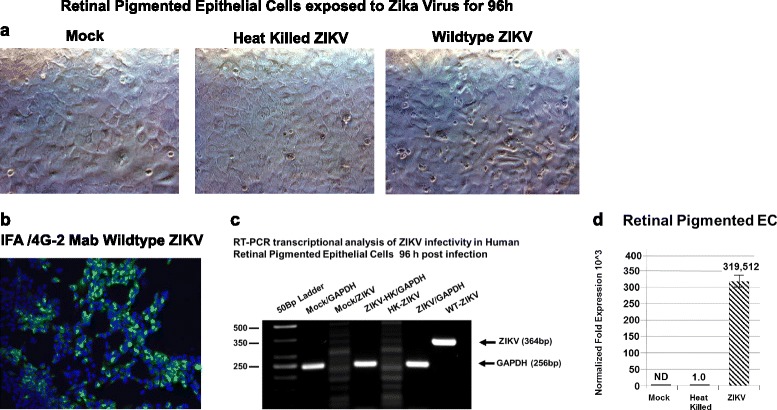
Retinal pigmented epithelial cells infectivity for ZIKV confirmed by RT-PCR. Phase contrast images of: a mock-infected confluent monolayer of retinal pigmented epithelial cells, a confluent monolayer of retinal pigmented epithelial cells exposed to heat-killed ZIKV, and retinal pigmented epithelial cells exposed to wild-type ZIKV. b Immunofluorescence staining of ZIKV-infected retinal pigmented epithelial cells with the Flavivirus 4G2 antibody. c Semiquantitative RT-PCR amplification of a 364-bp fragment using ZIKV-specific primers. GAPDH was amplified as a control represented as a 256-bp fragment. Phase and fluorescent images were taken on a Nikon TE2000S microscope mounted with a charge-coupled device (CCD) camera at ×200 magnification. For fluorescent images, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) was used to stain the nuclei blue. d qRT-PCR of ZIKV-infected retinal pigmented epithelial cells 96 h after infection. Mock-infected controls are shown, and all values were normalized to GAPDH
