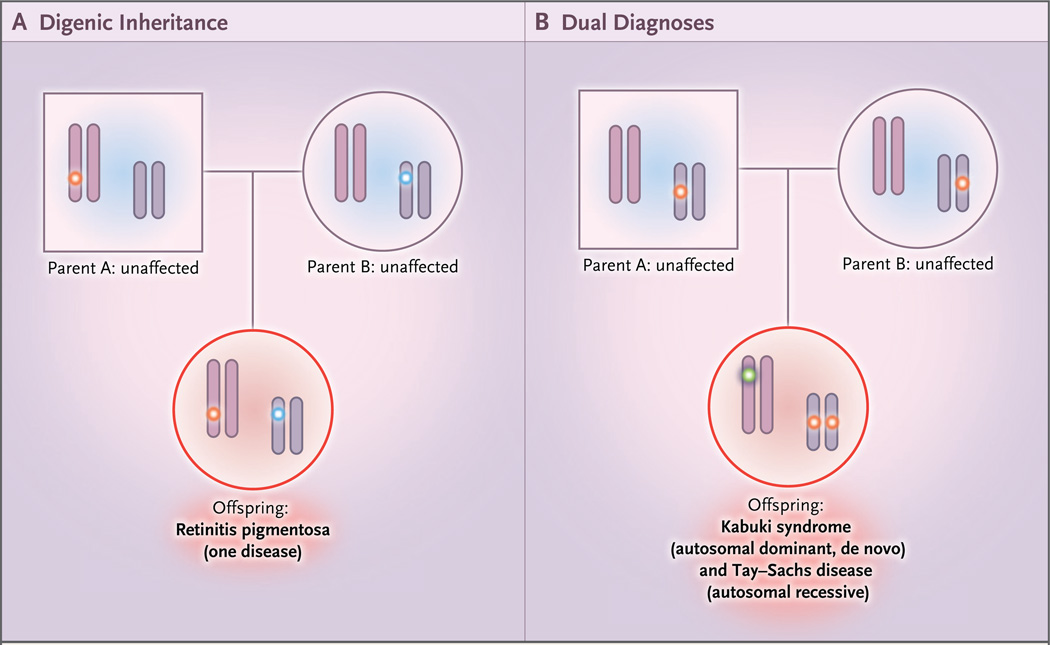
Figure 1. Models of Nonmendelian Inheritance.
Panel A shows digenic inheritance of pathogenic alleles at different loci from each parent, resulting in an affected offspring. Panel B shows dual molecular diagnoses — in this case, one homozygous pathogenic variant in a recessive disease gene inherited from each carrier parent and one de novo variant that resulted in a second, independent autosomal dominant disorder. Many combinations are possible: autosomal dominant plus autosomal dominant, autosomal dominant plus autosomal recessive, autosomal dominant plus X-linked, autosomal recessive plus autosomal recessive, autosomal recessive plus X-linked, and X-linked plus X-linked.