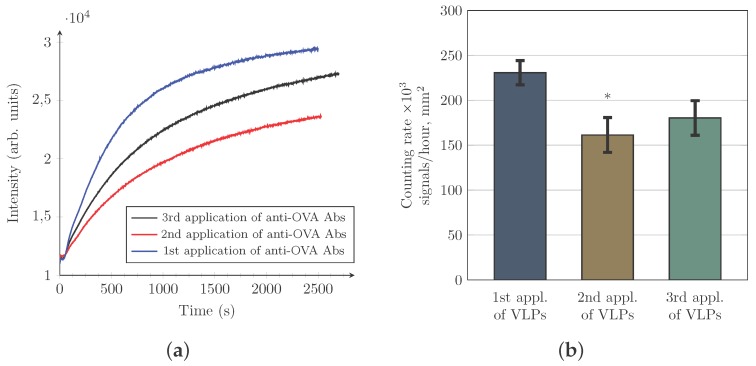
Figure 5.
Changes of virus-like particle (VLP) counting rates after repeated use of the same gold sensor were investigated. Sensor surface is functionalized with cysteine-conjugated protein A/G and further covered with anti-ovalbumin antibody. After the first coverage with antibody and a measurement of VLP counting rate, an elution of antibody layer is performed. Then, after recovery with Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) buffer, the second time coverage with anti-ovalbumin antibody and again a measurement of VLP counting rate are carried out. This cycle is repeated the third time. Three independent experiments were performed. The efficiency of antibody binding to the sensor surface is monitored and data are presented on the graph (a). The typical monitored antibody binding curves are displayed (for one experiment from three performed). Counting rates of HIV-VLPs are presented on the graph (b). Statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t-test. Significance was set at and marked with symbol “*” (significant difference between the first application of VLP and the second). (a) antibody binding efficiency; and (b) HIV-VLP counting rates.