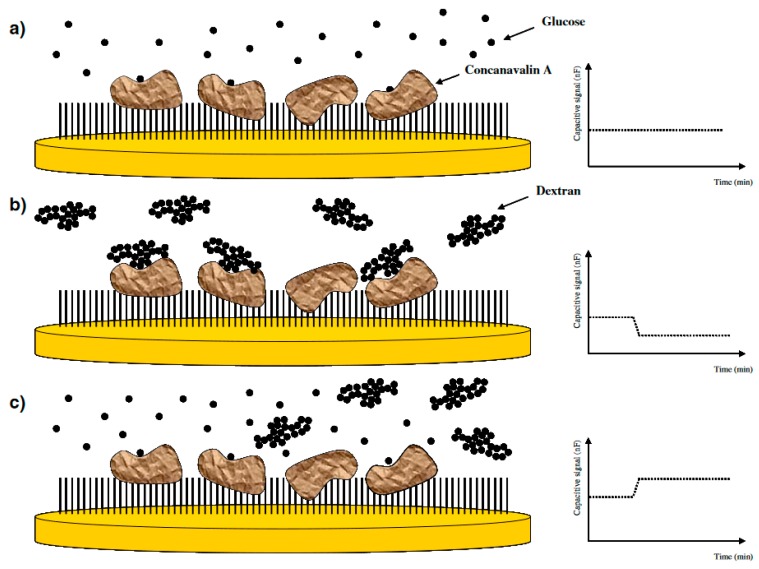
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the competitive glucose binding assay. (a) When glucose is injected into the capacitive system, it binds to the immobilized Concanavalin A (ConA) on the surface. However, this binding does not make any change in the capacitance level, as shown in the graph on the right, due to the small size of the glucose molecule; (b) When a glucose polymer (dextran) is injected into the system, binding of this big polymer to ConA results in a decrease in the capacitance signal; (c) When glucose is injected into the system again, displacement of dextran with glucose results in the capacitance turn back to the original baseline level. (Reproduced from Reference [22] with permission).