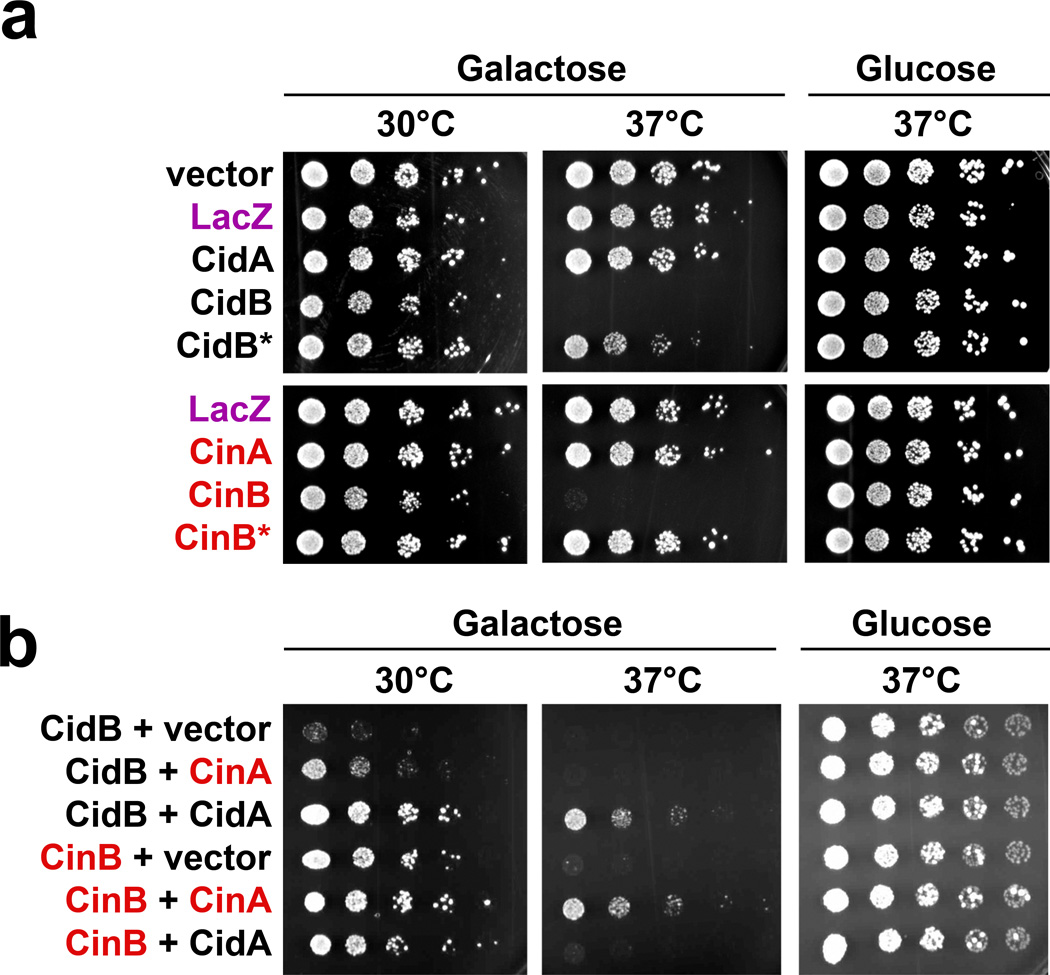
Figure 2.
Testing of the Modification-Rescue hypothesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. a. Expression of Wolbachia proteins from a galactose-inducible GAL1 promoter on minimal medium lacking uracil and containing galactose or glucose (3 replicates). Control plasmids pYES2 (empty vector) and LacZ (negative control) cause no defects. Both CidB and CinB expression blocks yeast growth at high temperature. Inactivation of the Ulp1-like protease by a C1025A mutation (CidB*) or the putative DUF1703 nuclease by mutation of the D-E-K triad to A-A-A (CinB*) eliminates toxicity. b. Coexpression of CidB or CinB with different upstream operon components on minimal media lacking uracil and leucine shows growth rescue only with cognate partners (3 replicates). Vector is pRS425.