Figure 3.
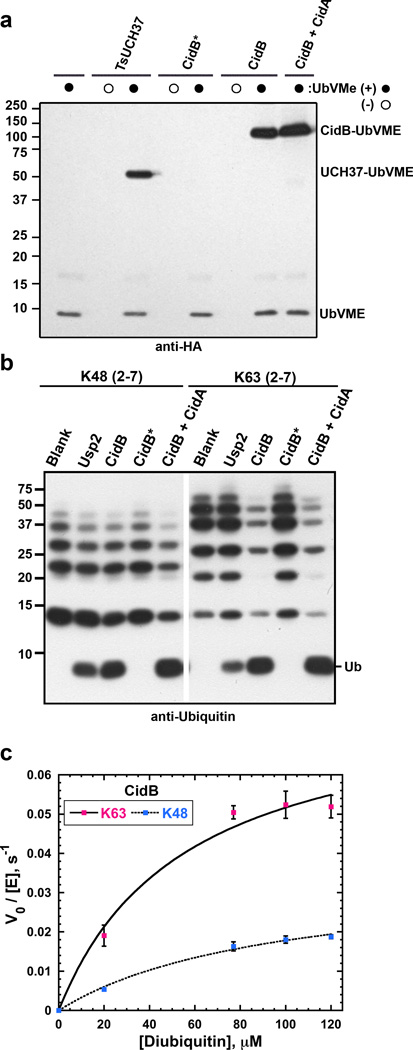
CidB is a DUB. a. DUB reactivity with the N-terminally HA-tagged suicide inhibitor, UbVME (3 replicates). Shown is an anti-HA immunoblot analysis of 30-min reactions performed at room temperature. UbVME reacts with the wild-type CidB protein but not the C1025A catalytic mutant (CidB*). TsUCH37 is a positive control.23 CidA at 100-fold molar excess does not inhibit UbVME reactivity. b. Cleavage by CidB of K48- and K63-linked ubiquitin chains assayed by anti-ubiquitin immunoblotting (3 replicates). Usp2 is a positive control.40 Enzyme and polyubiquitin chains were at 50 nM and 500 nM, respectively, and reactions were at 37°C for 1 h. c. CidB has a ~4-fold preference for K63-ubiquitin dimers compared to K48-linked dimers. Shown is a plot of initial velocity (divided by total enzyme concentration) as a function of substrate concentration from three independent experiments. Error bars are standard deviations.