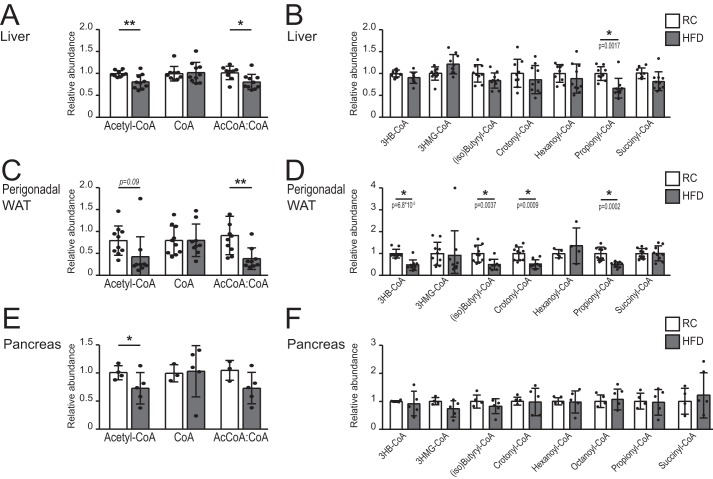
FIGURE 3.
Acetyl-CoA and/or the acetyl-CoA:CoA ratio is/are suppressed by HFD. A–F, quantification of acyl-CoA species in the liver (A and B; n = 9 for RC, n = 10 for HFD), perigonadal WAT (C and D; n = 10 for RC, n = 10 for HFD), and pancreas (E and F; n = 4 for RC, n = 5 for HFD) of mice fed with either RC (white columns) or HFD (gray columns) for 4 weeks. Acyl-CoA measurements were normalized to internal standards, as described under “Experimental Procedures” and expressed as relative levels, with RC mean set to 1. For acetyl-CoA, CoA, the ratio between relative abundance of acetyl-CoA and relative abundance of CoA for each animal is depicted. (iso)Butyryl-CoA shows the abundance of both isobutyryl-CoA and butyryl-CoA, as the two isomers could not be discriminated. Data are graphed as mean ± S.D., with data from individual animals represented as dots. For A, C, and E, statistical significance was assessed by two-tailed t test (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; or as indicated). For B, D, and F, significance was assessed by two-tailed t tests and corrected for multiple comparisons using the Holm-Sidak method (α = 0.05). The p values are indicated on the graphs.