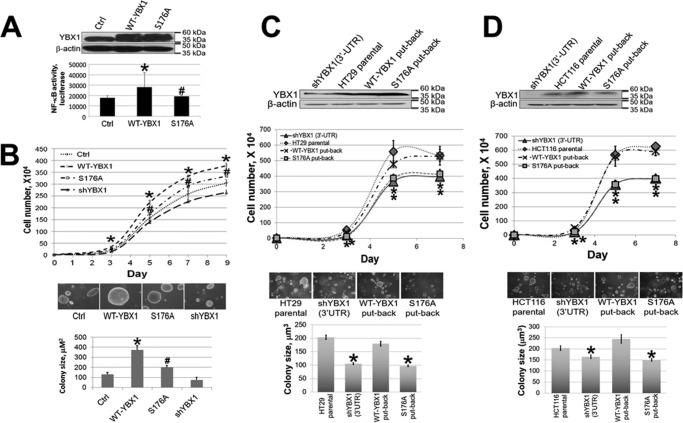
FIGURE 6.
Phosphorylation of Ser-176 of YBX1 plays a crucial role in promoting cell proliferation and anchorage-independent growth in human colon cancer cells. A, top panel, Western blot showing that overexpression of WT-YBX1 or the S176A mutant was at similar levels in HT29 cells. Bottom panel, luciferase assay showing that WT-YBX1 activated NF-κB, whereas the S176A mutation impaired the ability of YBX1 to activate NF-κB. *, p < 0.05 versus the Ctrl group; #, p < 0.05 versus the WT-YBX1 group. B, top panel, cell growth curve showing that overexpression of WT-YBX1 promoted cell growth compared with the Ctrl group, whereas using a pool of shRNA to knockdown YBX1 greatly slowed down cell growth. Moreover, the S176A mutation led to decreased cell growth compared with WT-YBX1 cells. *, p < 0.05 versus the Ctrl group; #, p < 0.05 versus the WT-YBX1 group. Center and bottom panels, anchorage-independent growth (soft agar) assay showing WT-YBX1 cells exhibited increased colony size compared with Ctrl cells. S176A mutant cells showed decreased colony size compared with WT-YBX1 cells. Furthermore, YBX1 shRNA knockdown led to decreased colony size compared with the Ctrl group. *, p < 0.05 versus the Ctrl group; #, p < 0.05 versus the WT-YBX1 group. C and D, first panels, Western blots showing that WT-YBX1 and S176A were expressed at similar levels as the parental HT29 cells (C) or HCT116 cells (D) in put-back cells (into their shYBX1 (3′-UTR) cells, respectively). Second panels, cell growth curves showing that S176A put-back cells displayed a similar cell growth rate as shYBX1 (3′-UTR) cells, whereas WT-YBX1 put-back cells completely rescued cell growth rate and showed similar cell growth rates as their parental HT29 cells (C) or HCT116 cells (D). *, p < 0.05 versus the parental cell group. Third and fourth panels, S176A put-back cells and shYBX1 (3′-UTR cells) had significantly reduced colony formation abilities compared with either parental HT29 cells (C) or HCT116 cells (D) or their WT-YBX1 put-back cells. * p < 0.05 versus the parental cell group.