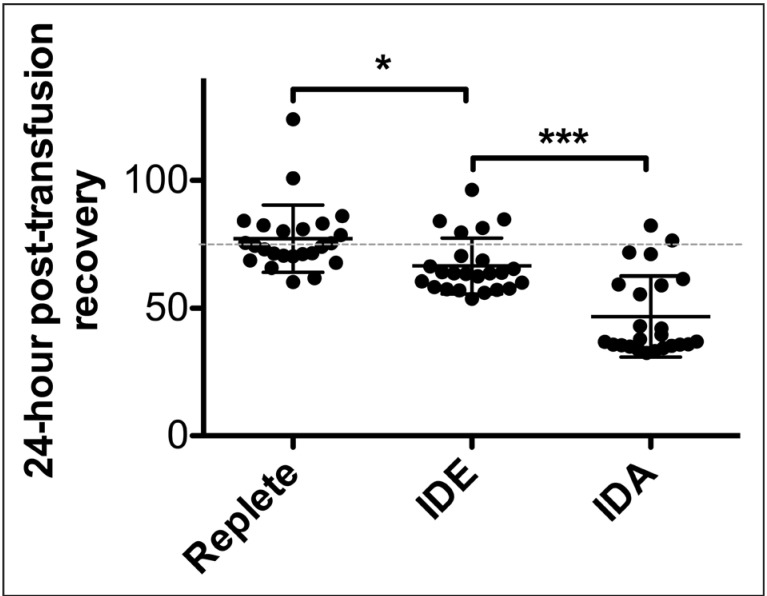
Figure 4.
Donor RBCs from mice with iron deficiency exhibit decreased 24-hour post-transfusion recovery.
Three groups of adult mice with varying iron status: iron replete, iron-deficient erythropoiesis with mild iron deficiency (IDE), and severe iron deficiency anaemia (IDA) were generated by modifying the iron-content of their diets with or without additional phlebotomy. At ~10 weeks of age, blood was collected from each cohort, pooled, leucoreduced, packed, and refrigerator-stored in CPDA-1 for 12 days. The 24-hour post-transfusion recoveries of the stored RBCs were quantified using flow cytometry in enhanced Green Fluorescent Protein-transgenic recipient mice. The experiment was repeated three times in its entirety (n=8 recipient mice per group per experiment; 24 mice per group total). Shown are the individual 24-hour post-transfusion recovery results for each recipient mouse, combined across all three replicate experiments. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001 by One-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparison test.