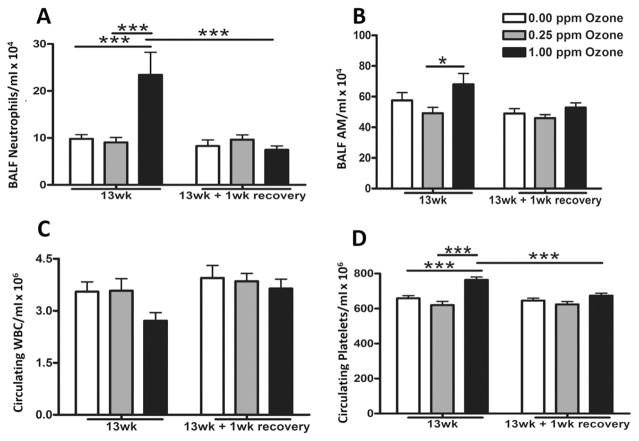
Fig. 9.
Subchronic ozone induced lung inflammation as determined by the assessment of cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). Lung inflammation was determined by analysis of cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) immediately after air, 0.25 ppm or 1.00 ppm ozone exposure at 13 wk and following a 1 wk recovery. BALF total cell count and cell differentials were performed to quantify (A) neutrophils and (B) alveolar macrophages (AM). Circulating (C) white blood cells (WBC) and (D) platelets were quantified using a Beckman-Coulter AcT blood analyzer. Values indicate mean ± SEM (n = 8–10). *Indicates differences between groups (*p ≤ 0.05, ***p ≤ 0.001).