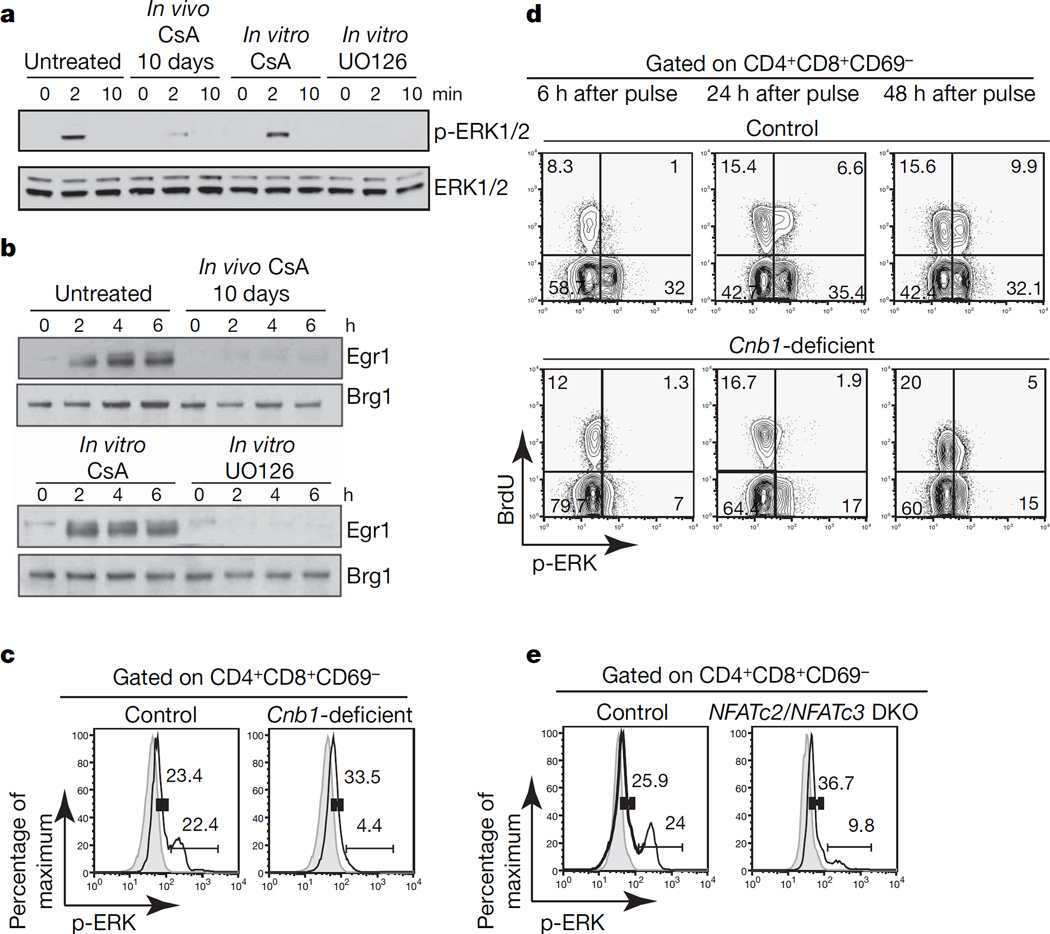
Figure 2. Developmental but not direct requirement for calcineurin/NFAT activity for proper activation of ERK.
a, ERK1/2 phosphorylation in double-positive cells from untreated and CsA-treated mice in the presence of CsA (200 ng ml−1) or UO126 (10 µM) after CD3ε crosslinking. b, Erg1 induction in double-positive cells from untreated or CsA-treated mice and in double-positive cells stimulated in the presence of CsA (200 ng ml−1) or UO126 (10 µM) after CD3ε crosslinking. Brg1 shows equal loading. c, ERK1/2 phosphorylation in double-positive CD69-negative Cnb1-deficient and control thymocytes after CD3ε crosslinking for 2 min (solid lines). Grey areas, unstimulated. d, BrdU incorporation and ERK1/2 phosphorylation in double-positive CD69-negative thymocytes from Cnb1-deficient mice and control littermates injected once with BrdU after CD3ε crosslinking for 2 min. The numbers in the corners of the panels represent the percentage of cells in each quadrant. e, ERK1/2 phosphorylation in NFATc2/NFATc3 double knockout (DKO) and control double-positive CD69-negative thymocytes after CD3ε crosslinking for 2 min (solid lines). Grey lines, unstimulated. The numbers in graphs c and e represent the percentage of cells in the indicated interval.