Figure 3.
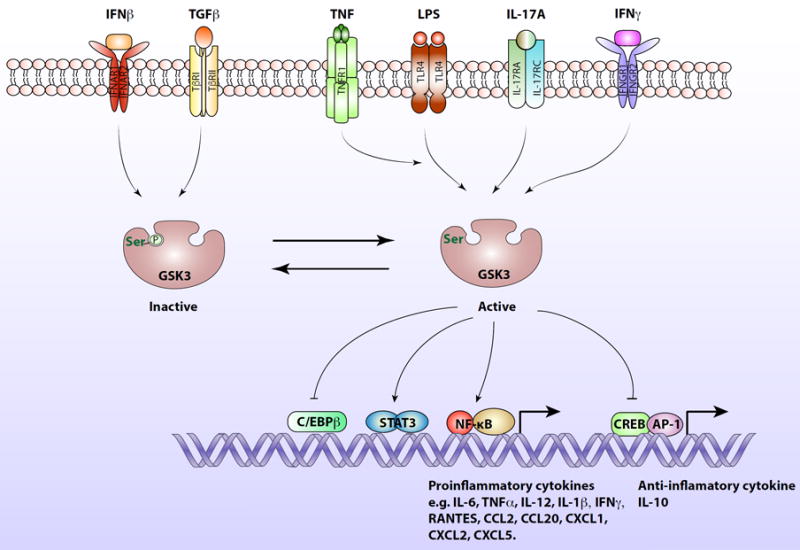
GSK3 is a central kinase in the inflammatory response.
Intracellular signaling induced by IFNβ and TGFβ promotes the inhibitory serine-phosphorylation of GSK3 on serine-9 of GSB3β and serine-21 on GSK3α, allowing the induction of IL-10 production by blocking the inhibitory effect of GSK3 on the CREB and AP-1 transcription factors that induce IL-10 expression. In contrast, signaling induced by LPS activates GSK3, which promotes NF-κB activation and translocation to the nucleus where it activates the expression of proinflammatory cytokines. Activated GSK3 also inhibits CREB and AP-1 transcriptional activities in response to LPS, diminishing production of the anti-inflammatory cytokine, IL-10. TNFα promotes the LPS-induced activation of GSK3. Several cytokines stimulate intracellular signaling pathways that regulate GSK3. For example, IL-17A stimulates signaling that activates GSK3, which causes inhibition of C/EBPβ transcriptional activity. GSK3 is also activated by IFNγ-stimulated signaling, and in response to IFNγ active GSK3 promotes STAT3 phosphorylation and activation, leading to its translocation to the nucleus where dimerized STAT3 induces the expression of proinflammatory cytokines.
