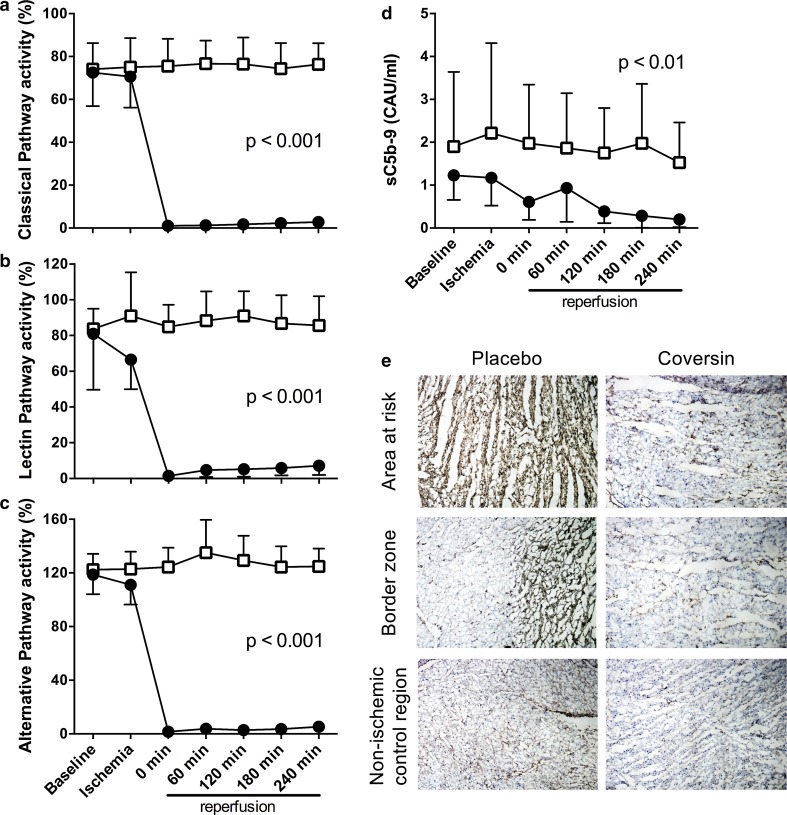
Fig. 5.
Coversin eliminated complement activity. Complement activity was assessed in plasma and the classical (a), lectin (b) and alternative pathway (c) were monitored using C5b-9 deposition as common readout. Coversin bolus treatment during coronary ischemia led to significantly reduced complement activity in all pathways (filled circles) and was not affected in control animals (open boxes). Complement activity remained low in all three pathways throughout the reperfusion period until the end of the experiment. Consequently, the plasma soluble complement activation product sC5b-9 was significantly reduced in plasma of coversin treated animals in comparison to controls (d). Myocardium was stained with an antibody against C5b-9 (e). Visually, deposition of C5b-9 (brown) was markedly decreased in the area at risk, the border zone and the non-ischemic control region in coversin treated animals in comparison to placebo treated animals. a–d Values presented as mean ± SD [n = 8 (placebo) and n = 7 (coversin)]. Linear mixed effect model. CAU complement arbitrary units. e Results of two representative animals are shown