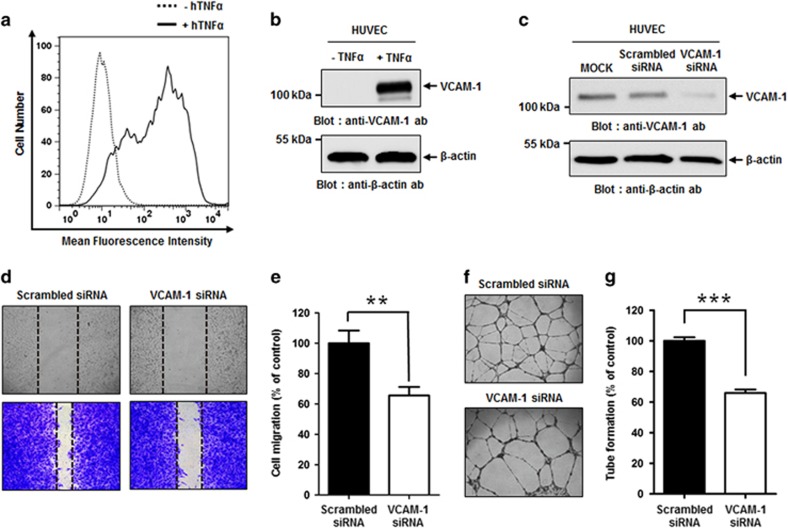
Figure 1.
Effect of VCAM-1 knockdown on HUVEC migration and tube formation. (a) HUVECs were incubated in EGM in the absence (dashed line) or presence (solid line) of 20 ng ml−1 hTNFα for 24 h. Cells were stained with anti-VCAM-1 monoclonal antibody, and VCAM-1 expression was analyzed using flow cytometry. (b) Representative immunoblot showing relative VCAM-1 expression levels on HUVECs cultured in EGM in the absence or presence of hTNFα. (c) Representative immunoblot showing relative VCAM-1 expression levels following mock transfection of HUVECs or transfection with scrambled siRNA or VCAM-1 siRNA cultured in EGM in the presence of hTNFα. β-actin was used as a loading control. (d) Light microscopy images depicting migration in wound healing assay of scrambled siRNA- or VCAM-1 siRNA-transfected HUVECs cultured in EGM in the presence of hTNFα. Images were captured at 0 h (top; unstained) and 10 h (bottom; stained with crystal violet). (e) Quantitation of migration of scrambled siRNA- or VCAM-1 siRNA-transfected HUVECs cultured in EGM in the presence of hTNFα, expressed as a percent of scrambled siRNA migration, based on the distance separating wound margins. (f) Light microscopic images depicting tube formation by scrambled siRNA- and VCAM-1 siRNA-transfected HUVECs cultured in EGM in the presence of hTNFα. (g) Quantitation of total tube branches in scrambled siRNA- or VCAM-1 siRNA-transfected HUVECs cultured in EGM in the presence of hTNFα, expressed as a percent of tube formation in the presence of scrambled siRNA. All data are presented as the mean±s.e.m. of triplicate measurements from one of the three independent experiments; **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.