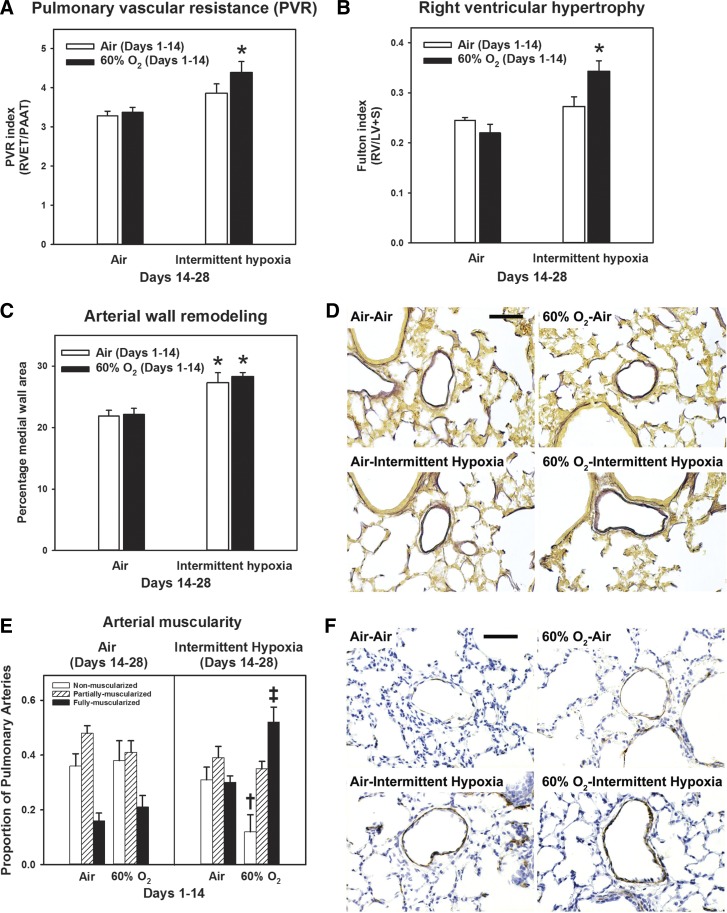
Fig. 3.
Changes in markers of pulmonary hypertension secondary to intermittent hypoxia. Rat pups were exposed to normoxia (Air) or hyperoxia (60% O2) from postnatal days 1 to 14 followed by recovery in normoxia (Air) or intermittent hypoxia (Intermittent hypoxia) until postnatal day 28. A: pulmonary vascular resistance index (n = 11–12 animals/group). B: Fulton index (right ventricular hypertrophy; n = 6 animals/group). C: percentage medial wall area (arterial wall remodeling; n = 6 animals/group). D: representative high-power photomicrographs of elastin-stained pulmonary arteries (bar length = 50 µm). E: muscularization of pulmonary arteries (n = 4–5 animals/group). F: representative high-power photomicrographs of α-smooth muscle actin-stained pulmonary arteries (bar length = 50 µm). Graph bars represent means ± SE. *P < 0.05, by ANOVA, compared with Air-Air and 60% O2-Air groups. †P < 0.05, by ANOVA, for nonmuscular arteries, compared with Air-Air and 60% O2-Air groups. ‡P < 0.05, by ANOVA, for fully muscularized arteries compared with all other groups.