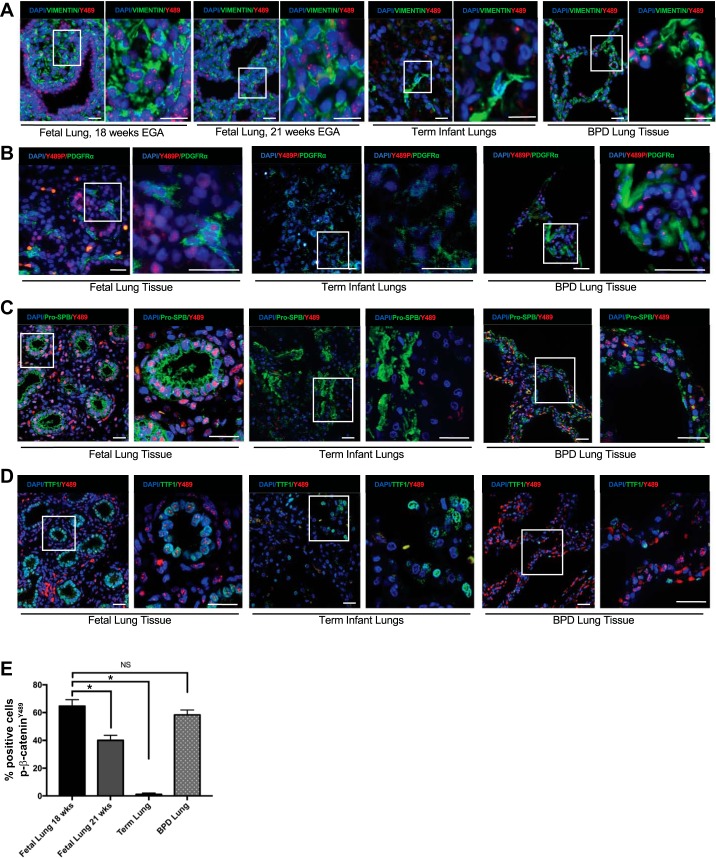
Fig. 1.
Phospho-Y489 β-catenin (p-β-cateninY489) localization in epithelial cells and fibroblasts during lung development and in BPD. A: IF for p-β-cateninY489 in fetal lung sections at 18 wk and 21 wk estimated gestational age, lungs from term infants who died without respiratory pathology, and the lungs with infants with BPD demonstrating nuclear presence of p-β-cateninY489 (red) in the fetal lung cells and BPD lungs. Some cells positive for p-β-cateninY489 also costained positive for vimentin (green), a marker of fibroblasts. B: IF for p-β-cateninY489 (red) and fibroblast marker PDGFRα (green) in fetal lungs (18 wk, term human lungs, and BPD lung tissue. C: IF for p-β-cateninY489 (red) and epithelial marker Pro-SPB (green) in fetal lungs (18 wk, term human lungs, and BPD lung tissue. D: IF for p-β-cateninY489 (red) and epithelial marker TTF1 (green) in fetal lungs (18 wk, term human lungs, and BPD lung tissue. Scale bar = 50 µm. E: quantification of percentage of cells positive for p-β-cateninY489; 10 high-powered fields were counted 3 times for each condition; *P < 0.001; NS, not significant.