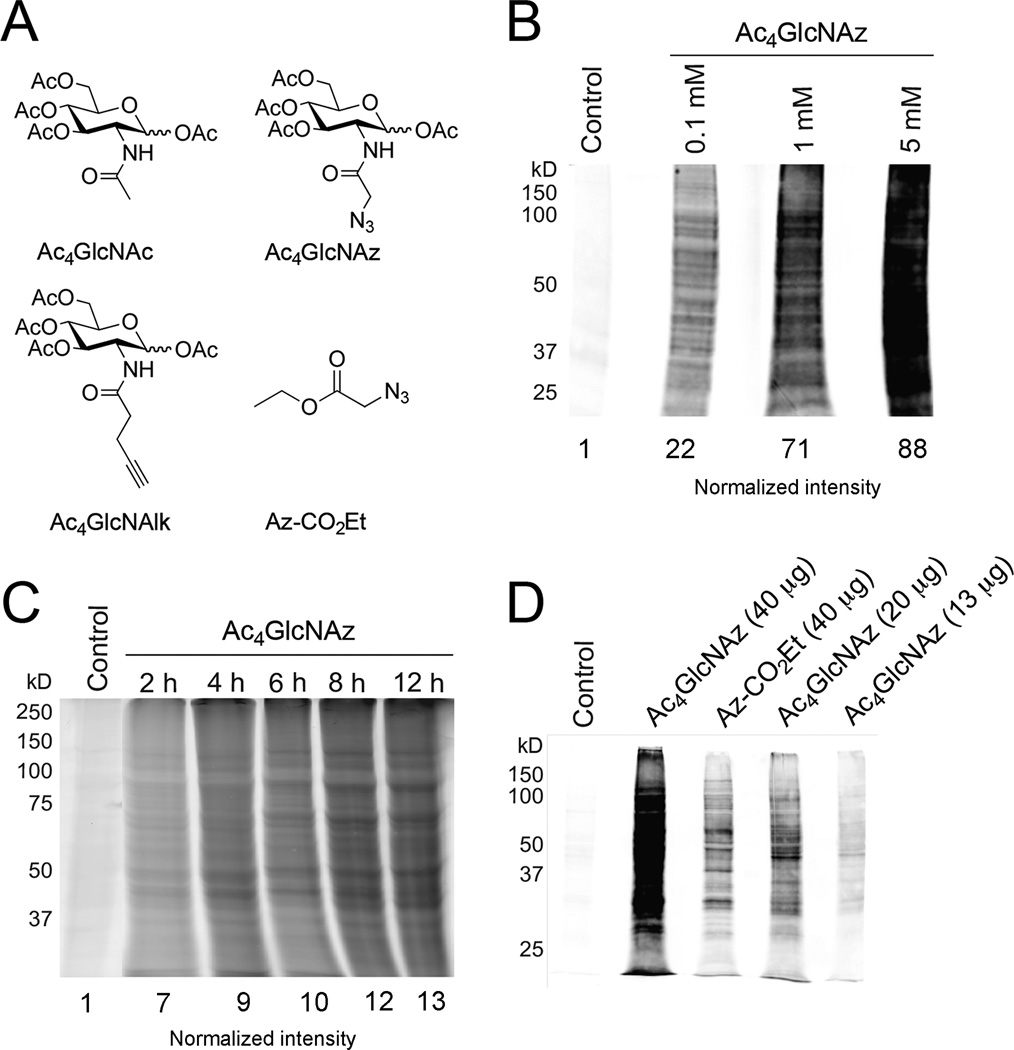
Figure 1. Toxoplasma tachyzoites metabolize unnatural sugars.
(A) Structures of peracetylated N-acetylglucosamine (Ac4GlcNAc) and the corresponding alkynyl (Ac4GlcNAlk) and azido (Ac4GlcNAz) analogs used in metabolic labeling studies. The acetyl groups facilitate sugar uptake into cells and are removed by the action of non-specific esterases in the cytoplasm. An azide-functionalized acyl chain (Az-CO2Et) used in various control experiments is also pictured. The azide and alkyne functional groups can be detected using bioorthogonal “click” chemistries. (B) Toxoplasma tachyzoites incorporate Ac4GlcNAz in a dose-dependent manner. Parasites were incubated with unnatural sugar (0.1–5 mM) or the control sugar Ac4GlcNAc for 8 hours, lysed, and reacted with a biotin-alk tag via “click” chemistry. The labeled proteins were separated via gel electrophoresis and detected via immunoblot with streptavidin. Equivalent protein loading was confirmed via staining with Ponceau S (Figure S1) and normalized intensities are listed. (C) Toxoplasma tachyzoites incorporate Ac4GlcNAz in a time-dependent manner. Parasites were incubated with Ac4GlcNAz (1 mM) or the control sugar Ac4GlcNAc (1 mM) for 2–12 h hours, lysed, and reacted with a rhodamine-alkyne probe. Labeled proteins were separated via gel electrophoresis and analyzed via in-gel fluorescence. Equivalent protein loading was confirmed via staining with Ponceau S (Figure S4) and normalized intensities are listed. (D) Ac4GlcNAz treatment reveals a unique glycoprotein fingerprint. Parasites were incubated with Ac4GlcNAz (1 mM), Ac4GlcNAc (1 h) or a non-sugar probe (Az-CO2Et) for 8 hours, lysed, and reacted with a biotin-alk tag. Labeled proteins were analyzed via immunoblot as in (C). Equivalent protein loading was confirmed via staining with Ponceau S (Figure S7).