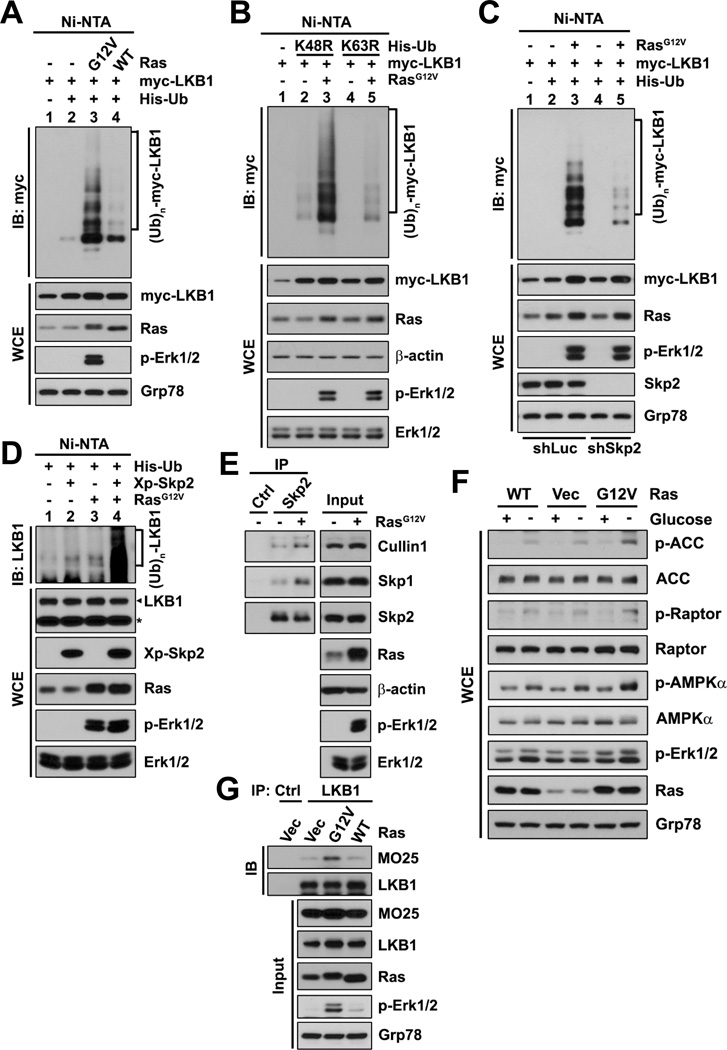
Figure 5. Oncogenic Ras induces K63-linked polyubiquitination of LKB1 and activation of the LKB1/AMPK signaling via Skp2.
(A–D) In vivo ubiquitination assays in HEK293T cells (A, B and D) or HEK293T cells with control or Skp2 knockdown (C) transfected with the indicated plasmids were followed by IB. The asterisk in (D) indicates non-specific bands (as loading controls), and the arrowhead indicates the bands corresponding to LKB1.
(E) IPs by anti-IgG control or anti-Skp2 antibody from HEK293T cells transfected with vector or H-Ras were subjected to IB.
(F) WT MEFs with stable transduction of vector or the indicated H-Ras cultured in the presence (+) or absence (−) of glucose were subjected to IB.
(G) IPs by anti-IgG control or anti-LKB1 antibody from Hep3B cells with stable transduction of vector or the indicated H-Ras were subjected to IB.
Phosphorylation of Erk1/2 indicates Ras activation.
See also Figure S5.