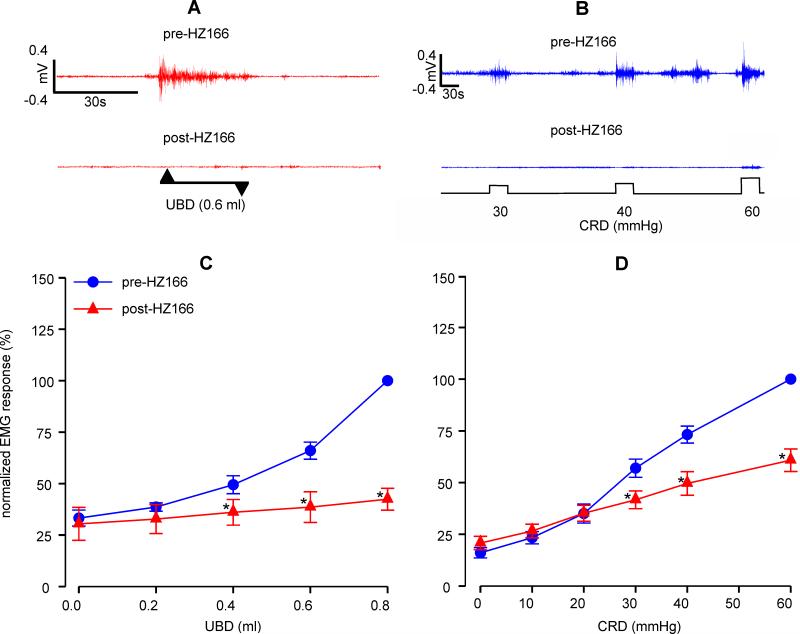
Fig. 1.
Effect of HZ166 (10 μg/animal) on the VMR of naïve adult rats. Representative EMG tracing pre- and post- intrathecal (i.t) administration of HZ166 to 0.6 ml of UBD (A) and 30-60 mmHg of CRD (B). VMR is represented as percentage normalized EMG response to either to phasic (0.2-0.8 ml) UBD or graded (10–60 mmHg) CRD. (C) Intrathecal administration of HZ166 significantly (n=6, p<0.001 vs pre-HZ166) decreased the VMR to UBD from 0.4 ml onwards. (D) Similarly, i.t administration of HZ166 also significantly (n=9, p<0.001 vs pre-HZ166) decreased the VMR to CRD from 20 mmHg pressure onwards. Values are expressed as mean ± S.E.M of ‘n’ animals in each group. p≤0.05 was considered significant. * compared with pre-HZ166 baseline.