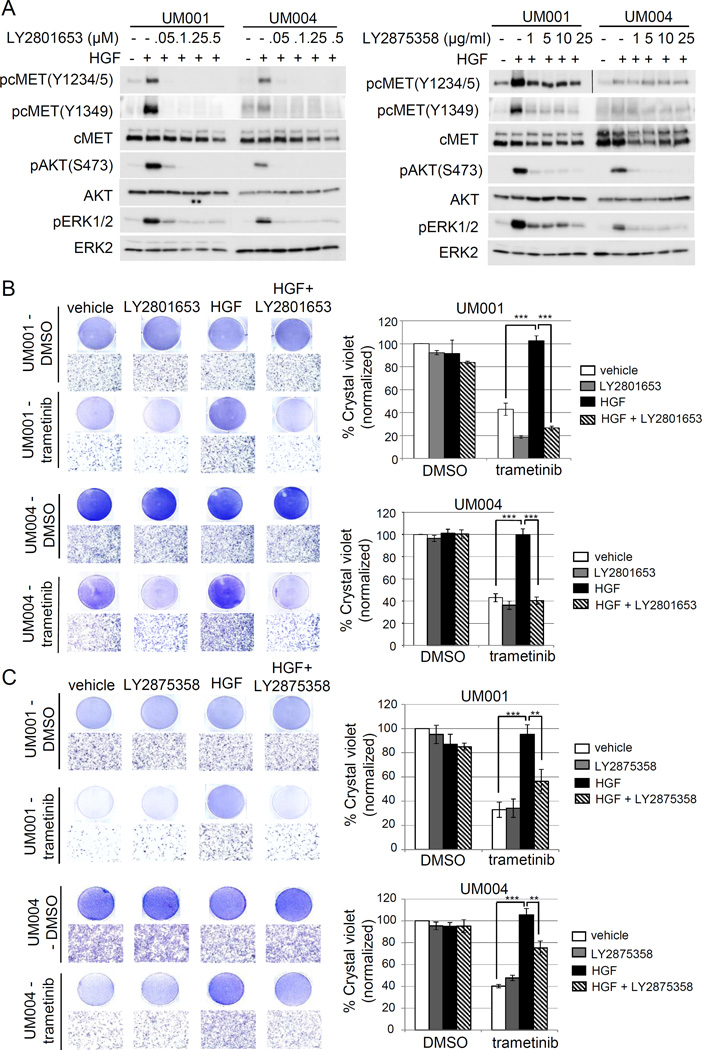
Figure 3. Clinical grade cMET targeting agents, LY2801653 and LY2875358, overcome HGF-mediated resistance to trametinib in UM cells.
(A) A dual cMET/RON small-molecule inhibitor LY2801653 and a bivalent cMET monoclonal antibody LY2875358 block HGF/cMET signaling. UM001 cells and UM004 cells were pretreated with increasing doses of LY2801653 (left) and LY2875358 (right) overnight. The next day cells were stimulated with 10 ng/ml HGF for 30 minutes. Phosphorylation of cMET, AKT and ERK1/2 was assessed by Western blotting. (B) HGF-induced resistance to trametinib is reversed by LY2801653. UM001 cells (top) and UM004 cells (bottom) were treated with DMSO or 50 nM trametinib, in combination with 10 ng/ml HGF and/or 100 nM of LY2801643 as indicated for 48 hours (UM004) or 72 hours (UM001). Cells were washed and stained with crystal violet. Images were taken (100 × magnification). Scale bar is equal to 100 µm. The mean of percentage crystal violet from triplicate experiments following normalization to vehicle control is shown. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
(C) HGF-induced resistance to trametinib is reversed by LY2875358. UM001 cells (top) and UM004 cells (bottom) were first treated with 10 µg/ml LY2875358 for 45 min, followed by 10 ng/ml HGF and 50 nM trametinib for 48 hours (UM004) or 72 hours (UM001). Cells were stained with crystal violet. Representative microscopic images are shown (100 × magnification). Scale bar is equal to 100 µm. The percentage of crystal violet is normalized to vehicle control and the mean of percentage crystal violet from triplicate experiments is shown. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.