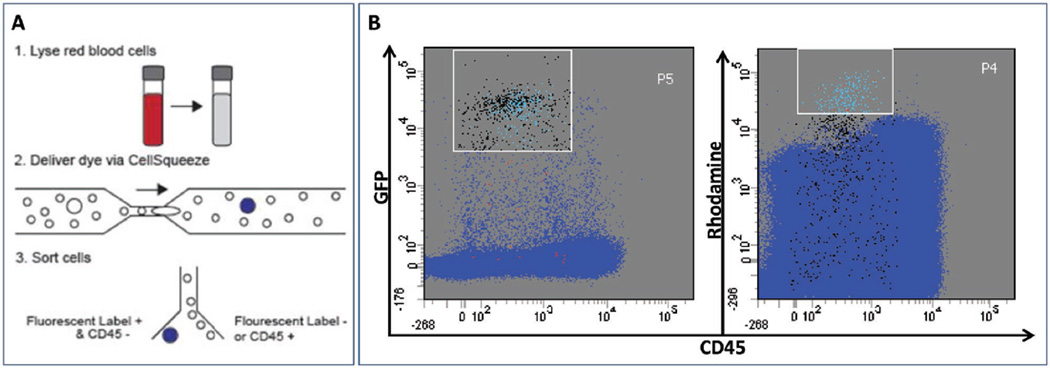
Figure 3.
Selective labeling of blood spiked with tumor cells. A) Schematic diagram for CTC isolation from whole blood. 1. GFP-expressing PANC-1 cells were spiked into whole blood and then depleted of red blood cells. 2. Red blood cell-depleted sample was delivered through device in the presence of tetramethylrhodamine dextran-labeled dye. 3. Cells were counterstained with an anti-CD45 antibody (APC) and GFP-positive CD45-negative cells were isolated by FACS. B) FACS plot demonstrating high specificity in tagging PANC-1 cells when PANC-1 cells are spiked into whole blood at high concentration (2000 cells per mL). GFP-expressing PANC-1 cells tagged with the rhodamine fluorophore were independently verified based on GFP fluorescence. The P4 gate [high rhodamine, low CD45 region] was used as a basis for sorting high candidate CTCs, and the P5 gate [high GFP, low CD45 region] was used to sort for GFP-expressing PANC-1 cells. The light blue dots within P5 are accurate hits (i.e., cells that are present within both P4 & P5 gates), such that those are GFP-expressing PANC-1 cells with intracellular rhodamine; 92% of the cells within P4 are accurate hits. False positive hits are red, and false negative hits are black. Within a mixture of about 1.2 million viable cells, we were able to isolate 227 GFP-expressing PANC-1 cells using the size-selective delivery platform.