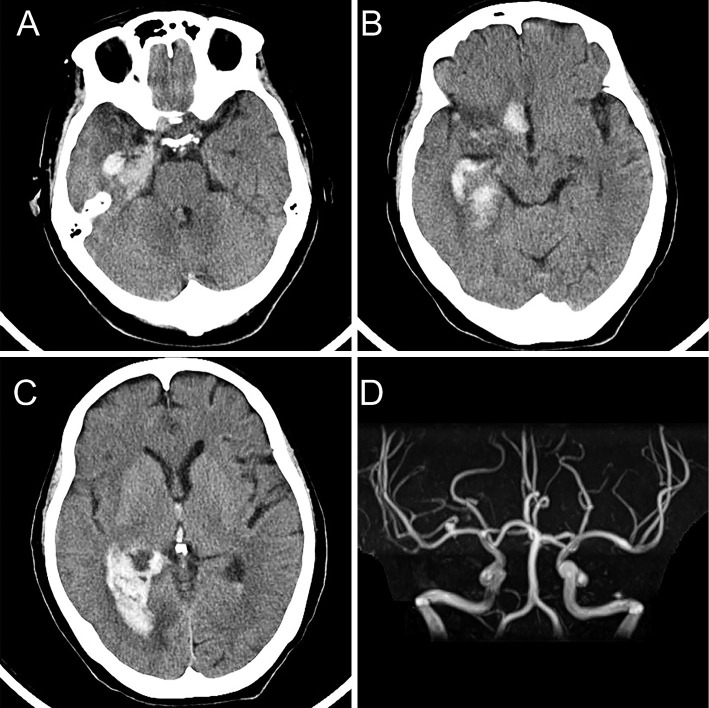
Figure 2.
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging at the time of cerebral hemorrhage. Axial computed tomography shows acute cerebral hemorrhage in the right medial temporal lobe (A) and the right basal frontal area (B). A right lateral ventricular rupture is also observed (C). Magnetic resonance angiography (D) shows an increase in the size of the right cerebral arterial aneurysm at the bifurcation of the distal M1 segment of the right cerebral artery.