FIGURE 3.
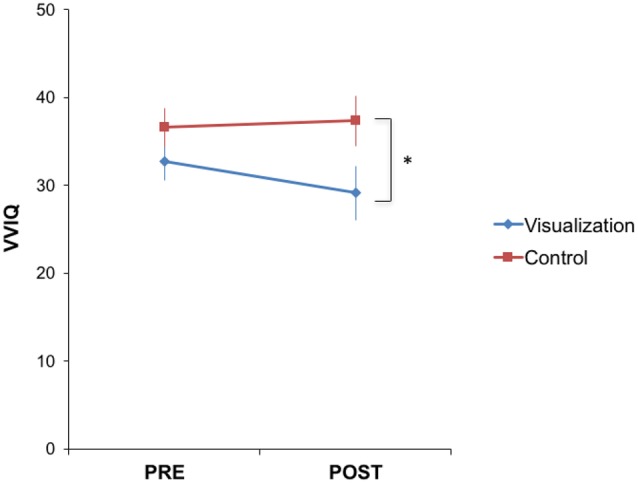
Visualization training tended to decrease VVIQ. The visualization group had significantly lower VVIQ scores (i.e., were more vivid visualizers) after training [t(36) = 2.20, p = 0.03], while there was no significant difference between the two groups before training [t(36) = 1.07, p = 0.29]. However, there was no significant effect of training within either group [t(19) = 1.54, p = 0.14 for visualization and t(17) = 0.81, p = 0.43 for control], and the interaction between group and time on VVIQ did not reach significance [t(36) = -1.66, p = 0.11]. ∗p < 0.05.
