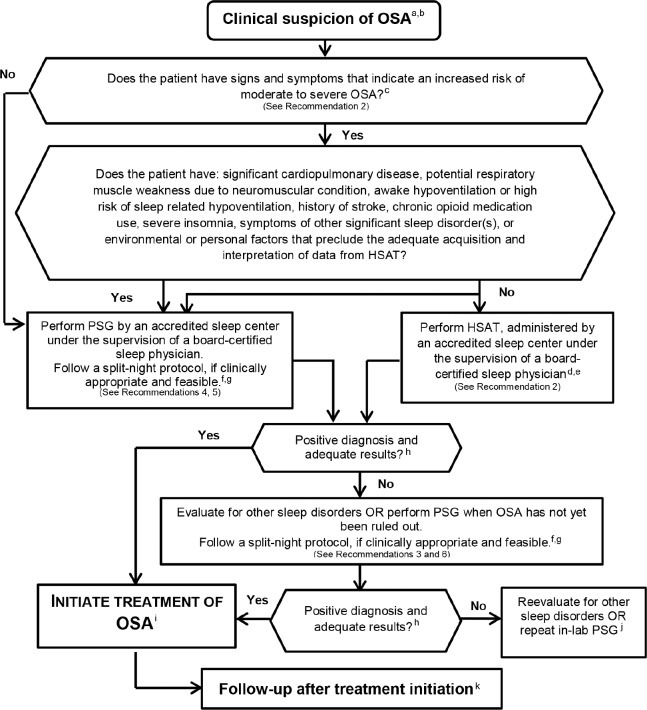
Figure 2. Clinical algorithm for implementation of clinical practice guidelines.
a = Clinical suspicion based on a comprehensive sleep evaluation. b = Clinical tools, questionnaires and prediction algorithms should not be used to diagnose OSA in adults, in the absence of PSG or HSAT. c = Increased risk of moderate to severe OSA is indicated by the presence of excessive daytime sleepiness and at least two of the following three criteria: habitual loud snoring; witnessed apnea or gasping or choking; or diagnosed hypertension. d = This recommendation is based on conducting a single HSAT recording over at least one night. e = This recommendation is based on HSAT devices that incorporate a minimum of the following sensors: nasal pressure, chest and abdominal respiratory inductance plethysmography (RIP) and oximetry; or peripheral arterial tonometry (PAT) with oximetry and actigraphy. For additional information, refer to The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events. f = A split-night protocol should only be conducted when the following criteria are met: (1) A moderate to severe degree of OSA is observed during a minimum of 2 hours of recording time on the diagnostic PSG; AND (2) At least 3 hours are available to complete CPAP titration. If these criteria are not met, a full-night diagnostic protocol should be followed. g = Clinically appropriate is defined as the absence of conditions identified by the clinician that are likely to interfere with successful diagnosis and treatment using a split-night protocol. h = A technically adequate HSAT includes a minimum of 4 hours of technically adequate oximetry and flow data, obtained during a recording attempt that encompasses the habitual sleep period. For additional information, refer to The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events. i = Treatment of OSA should be initiated based on technically adequate PSG or HSAT study. j = Consider repeat in-laboratory PSG if clinical suspicion of OSA remains. k = There should be early follow-up after initiation of therapy.