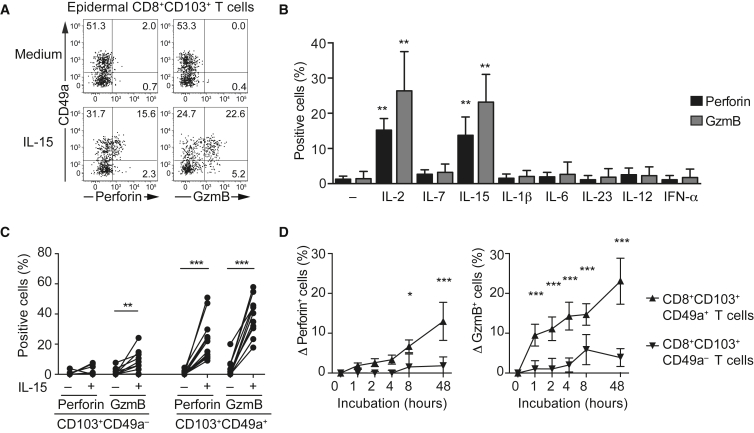
Figure 3.
IL-2 and IL-15 Induce Perforin and Granzyme Expression Specifically in Epidermal CD8+CD103+CD49a+ T Cells
(A) Representative FACS plot of perforin and granzyme B expression in relation to CD49a expression in epidermal CD8+CD103+ Trm cells with or without IL-15 (20 ng/mL) stimulation for 48 hr.
(B) Perforin (black) and granzyme B (gray) expressing cells among epidermal CD8+CD103+ Trm cells following 48 hr incubation with medium, IL-2 (20 ng/ml), IL-7 (20 ng/ml), IL-15 (20 ng/ml), IL-1β (20 ng/ml), IL-6 (20 ng/ml), IL-23 (20 ng/ml), IL-12, (50 ng/ml), IFN-α (2,000 U/ml). Mean ± SD is depicted. Kruskal-Wallis with Dunn’s multiple comparison tests.
(C) Proportion of perforin and granzyme B expressing cells among epidermal CD8+CD103+CD49a– or CD8+CD103+CD49a+ Trm cells upon IL-15 stimulation (n = 12). Two-tailed Wilcoxon test.
(D) CD8+CD103+ Trm cells were sorted and stimulated with IL-15 (20 ng/ml) for 1, 2, 4, 8, or 48 hr. Mean ± SD of the increase (Δ) in perforin (left) and granzyme B (right) expressing cells among CD8+CD103+CD49a– (inverted triangle) or CD8+CD103+CD49a+ (upright triangle) Trm cells as compared to unstimulated (n = 4). Two-tailed paired t test with Holm-Sidak correction. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. See also Figure S2.