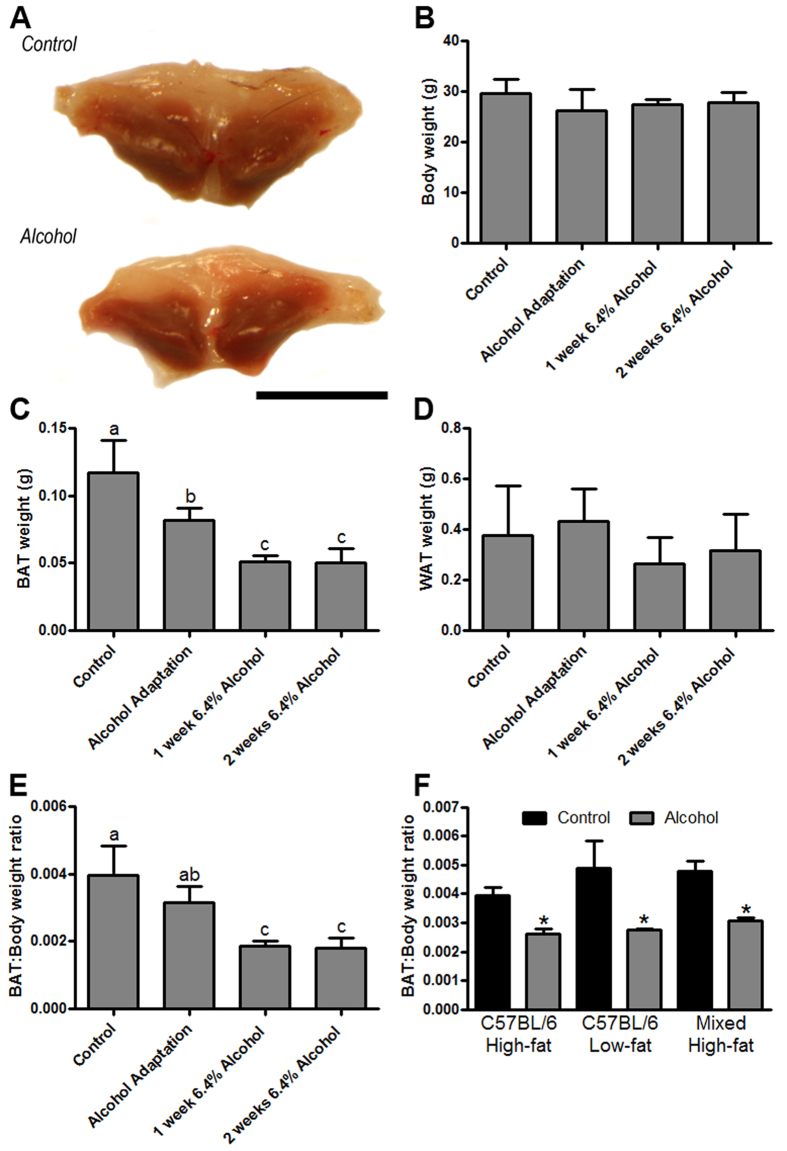
Figure 1. Chronic alcohol consumption decreases BAT mass.
The dissected intrascapular BAT depot of alcohol fed mice is visibly smaller (A). Body weight was not changed in mice chronically consuming alcohol (B); however, BAT weight was significantly decreased throughout the alcohol feeding period, which was verified by analyzing the BAT:Body weight ratio (E). There was no significant change in the weight of the epididymal white adipose tissue (WAT) depot weight (D). Follow-up studies show that alcohol’s ability to decrease BAT mass occurs independently of dietary fat content, or genetic background (F). (B–E) analyzed by one-way ANOVA; bars with different letters are significantly different; p < 0.05. (F) analyzed by Student’s t-test; *p < 0.05. Sample size: (B–E), control n = 12, all alcohol groups n = 6; (F) all groups n = 5–6.