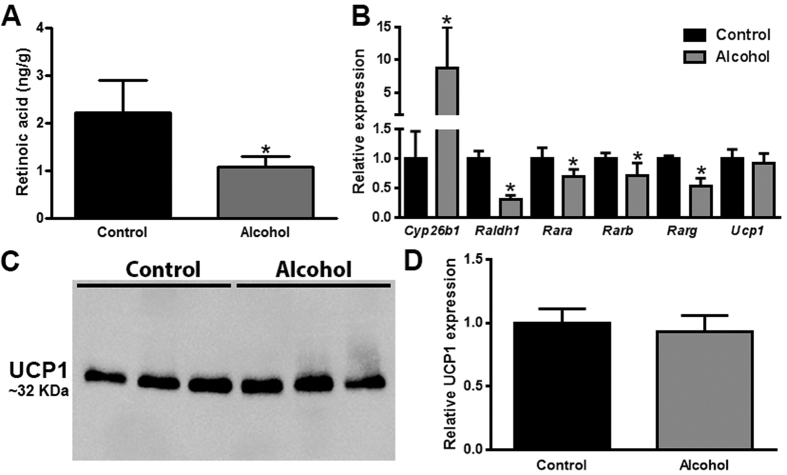
Figure 5. Chronic alcohol consumption is associated with decreased retinoid signaling in BAT, but no change in UCP1 expression.
The concentration of retinoid acid in the BAT of alcohol-fed mice is significantly decreased (A). The mRNA expression levels of genes involved in retinoid metabolism are significantly dysregulated in the BAT of alcohol consuming mice. The mRNA expression level of UCP1 was unchanged in alcohol-fed mice (B), this was confirmed at the protein level as shown by a representative western blot of UCP1 expression in BAT of control and alcohol-fed mice (C), with accompanying relative quantification normalized to total protein, as described in the methods (D). (A,B,D): analyzed by Student’s t-test; *p < 0.05. Sample size: (A) control n = 4, alcohol n = 6; (B) all groups n = 6; (C) all groups n = 3.