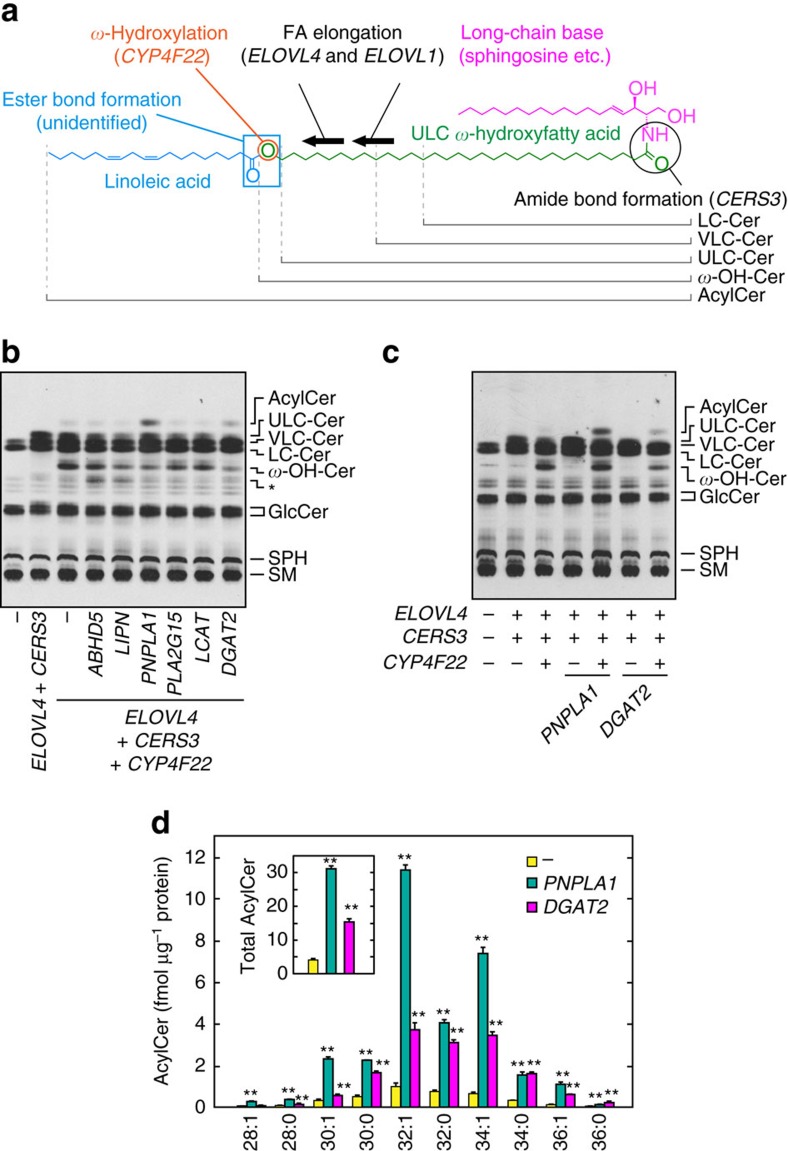
Figure 1. PNPLA1 is involved in acylceramide synthesis.
(a) Structure of acylceramide and genes involved in its synthesis. AcylCer, acylceramide; Cer, ceramide; ω-OH-Cer, ULC ω-hydroxyceramide. (b,c) HEK 293T cells were transfected with the plasmids encoding the indicated genes. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were labelled with [3H]sphingosine for 6 h at 37 °C in the presence of 10 μM linoleic acid. Lipids were extracted, separated by normal-phase TLC and detected by autoradiography. GlcCer, glucosylceramide; SM, sphingomyelin; SPH, sphingosine. The asterisk indicates an undetermined lipid, the production of which was not reproducible. Five independent experiments gave similar results, and a representative result is shown. (d) HEK 293T cells were transfected with an empty vector or the plasmid encoding 3xFLAG-PNPLA1 or 3xFLAG-DGAT2, together with the plasmids encoding 3xFLAG-ELOVL4, 3xFLAG-CERS3 and 3xFLAG-CYP4F22. Three hours after transfection, 10 μM linoleic acid was added to the medium and incubated for 24 h at 37 °C. Lipids were extracted and subjected to LC-MS/MS analysis. Acylceramides were detected by MRM mode and quantified using MassLynx software. The graph depicts the amount of each acylceramide species with the indicated FA chain-length. The inset represents the total acylceramide levels. Values represent the means±s.d.s of three independent experiments. Statistically significant differences compared to control cells are indicated (two-tailed Student's t-test; **P<0.01).