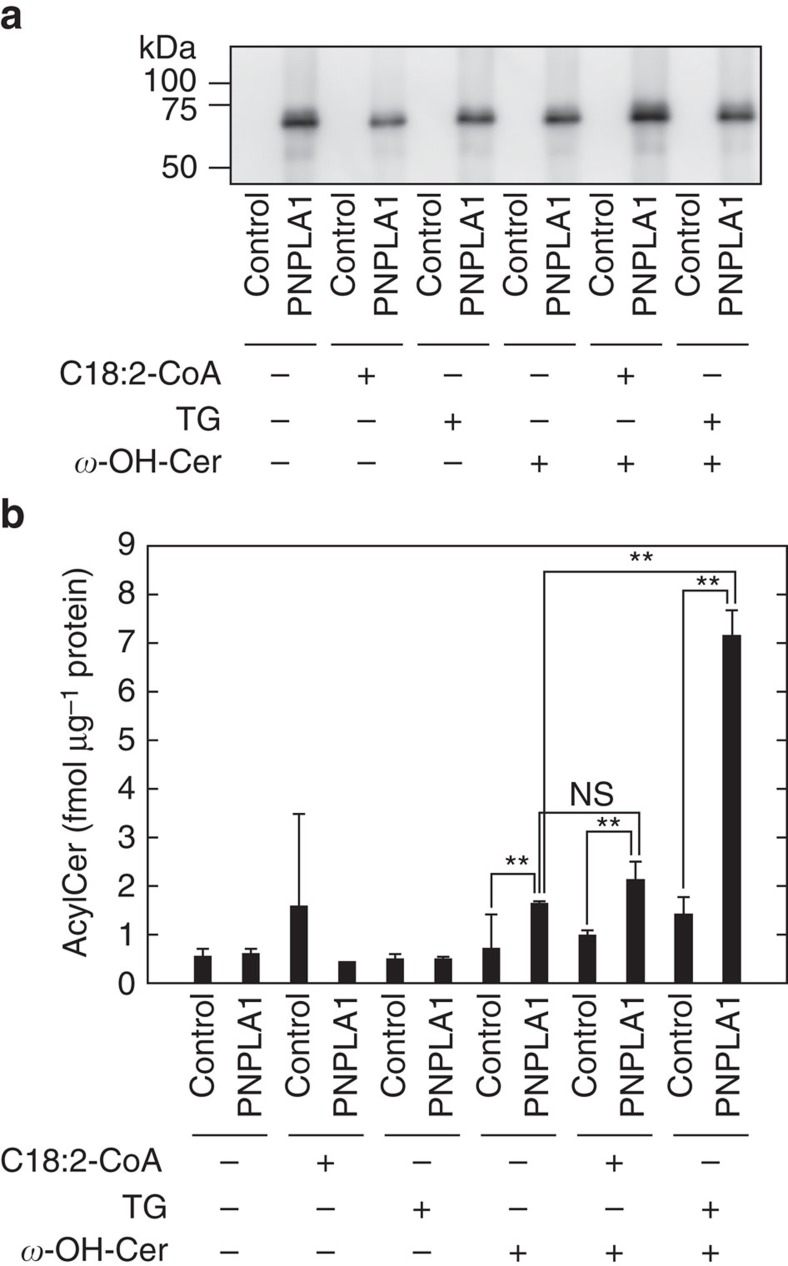
Figure 5. PNPLA1 catalyses acylceramide synthesis via transacylation.
SP6 RNA polymerase was used in vitro to transcribe genes from control plasmid (pEU-E01-T1R1) or plasmid encoding wild-type PNPLA1 (pEU-E01-3xFLAG-PNPLA1). The resulting mRNAs were then incubated with wheat germ lysates and phosphatidylcholine-based liposomes containing linoleoyl-CoA (C18:2-CoA), TG, and C30:0 ω-hydroxyceramide (ω-OH-Cer) as indicated, producing proteoliposomes. Proteoliposomes were then recovered by centrifugation. (a) Proteins associated with the prepared proteoliposomes were subjected to immunoblotting with anti-FLAG-antibody. An uncropped scan of the blot is provided as Supplementary Fig. 3. (b) An in vitro acylceramide synthesis assay was performed by incubating proteoliposomes for 1 h at 37 °C. Lipids were extracted, and the C30:0 acylceramide EOS was quantified by LC-MS/MS analysis. Values represent the means±s.d.s of three independent experiments. Statistically significant differences are indicated (two-tailed Student's t-test; **P<0.01). NS, not significant.