Figure 1.
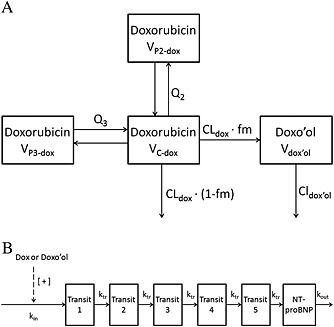
Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic structural models. A. Pharmacokinetic model for doxorubicin (dox) and doxorubicinol (doxo'ol). CLdox and CLdoxo'ol, elimination clearance of dox and doxo'ol, respectively; fm, fraction metabolized to doxo'ol; Q2 and Q3, intercompartmental clearances of doxorubicin; VC‐dox, VP2‐dox and VP3‐dox, the volume of distribution of doxorubicin for central and two peripheral compartments, respectively; Vdoxo'ol, the volume of distribution of doxo'ol. B. Pharmacodynamic model of doxorubicin‐induced N‐terminal pro‐brain natriuretic peptide (NT‐proBNP) production. [+ ]: stimulatory effect; dox, doxorubicin; doxo'ol, doxorubicinol; kin, production rate of the first step in NT‐proBNP synthesis pathway; kout, degradation rate constant of NT‐proBNP synthesis pathway; ktr, transit rate constant; NT‐proBNP, NT‐proBNP compartment; Transit 1–5, transit compartment 1–5
