Figure 3.
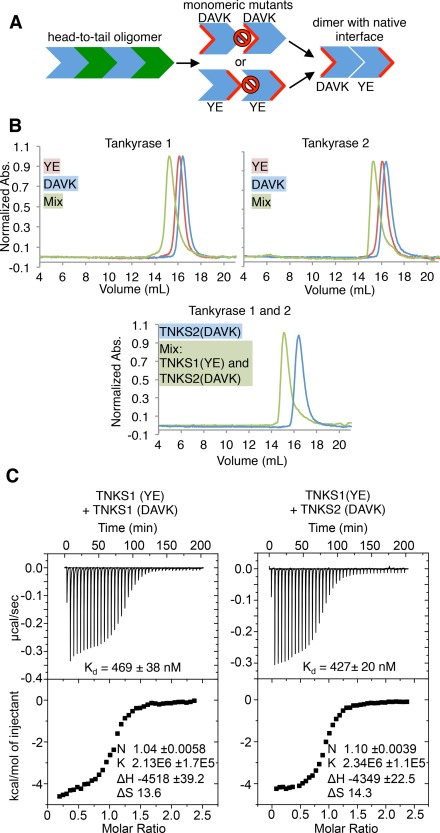
Tankyrase 1/2 SAM form strong homo and hetero‐oligomers. (A) Conceptual schematic of experiments in Figure 3. Residues are mutated on one face of the oligomeric interface to generate monomers (center). Complementary monomers can be mixed to generate dimers (right). Red indicates mutated surface. Prohibition signs indicate “no binding”. YE, TNKS1 Y1073E or TNKS2 Y920E; DAVK, TNKS1 D1055A/V1056K, or TNKS2 D902A/V903K. (B) Size exclusion chromatography (SEC) chromatograms of tankyrase 1 (top left) and tankyrase 2 (top right) SAM‐PARP YE and DAVK mutants. (Bottom) SEC trace of a 1:1 mixture of SAM‐PARP TNKS1 YE and TNKS2 DAVK, with TNKS2 DAVK elution profile shown as a reference. The maximum absorbance at 280 nm (y‐axis) is normalized to 1 for each trace. (C) Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) of TNKS1 SAM‐Linker YE with DAVK mutants (left; K d of 469 ± 38 nM), and TNKS1 SAM‐Linker(YE) with TNKS2 SAM‐Linker(DAVK) (right; K d of 427 ± 20 nM). K d, dissociation constants.
