Figure 2.
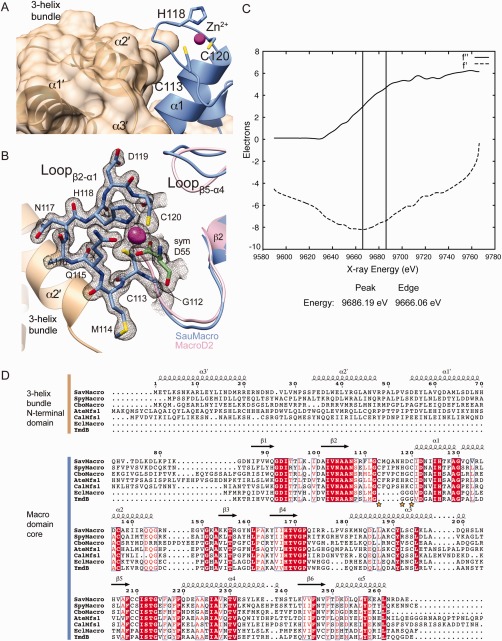
SauMacro Zn binding site. A. Packing of the three‐helix bundle with the Zn2+ binding site. Amino‐terminal helices α1′–α3′ are shown as ribbons and molecular surface (tan), carboxy‐terminal macrodomain is shown as ribbons (blue), with Zn2+ as a sphere (magenta). B. Close‐up view of Zn2+ binding site. SauMacro (blue) insertion loop residues are rendered as sticks, and the corresponding final 2mFo‐Dfc electron density map to 1.75‐Å resolution, contoured to 2σ is depicted as a mesh (gray). The location of the Zn2+ is revealed by the same 2mFo‐Dfc electron density map contoured at 10σ and depicted as a solid surface (magenta). SauMacro amino‐terminal helices (tan) and carboxy‐terminal helix α1 and Lβ5‐α4 (blue), as well as MacroD2 (PDB: 4IQY) α1 and Lβ5‐α4 are rendered as ribbons. C. X‐ray fluorescence scan at the Zn‐edge of purified, ammonium sulfate precipitated SauMacro protein. Anomalous scattering factors from X‐ray fluorescence f'' and derived from Kramers–Kronig (f') are consistent with the presence of Zn in our purified samples. D. Sequence comparison of SauMacro and related proteins (also see Table II). Sequence numbers and secondary structure assignments correspond to SauMacro. Red outlines indicate identical conservation, red letters indicate strong conservation (0.8 threashold). Yellow stars indicate Zn2+ binding residues in SauMacro. AteMfs1 and CalMfs1 contain additional carboxy‐terminal sequence corresponding to a fused sirtuin protein. EclMacro and YmdB lack amino‐terminal extensions and the conserved Zn2+ binding site.
