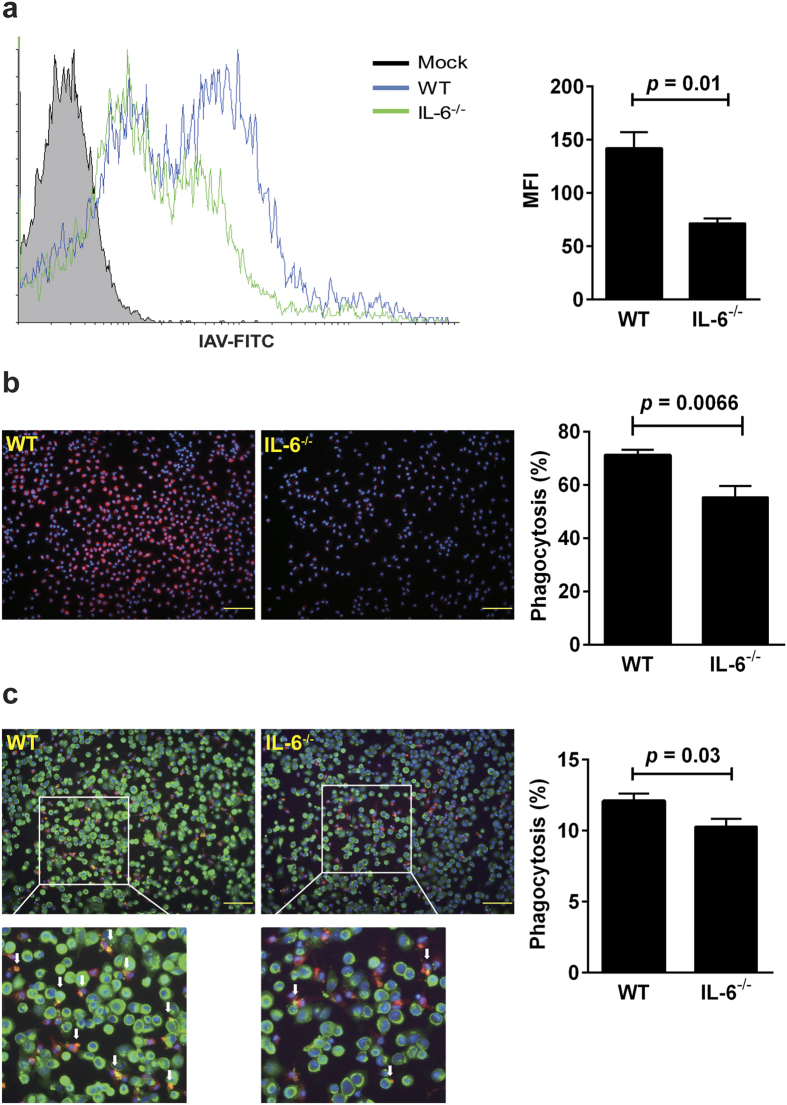
Figure 6. IL-6 deficiency reduces phagocytic activities of macrophages.
The phagocytic activities of elicited macrophages collected from WT and IL-6−/− mice were assessed for their uptakes of FITC-labeled IAV (a), QD649 quantum dot particles (b) and IAV-infected MDCK cells (c). (a) Phagocytosis of FITC-labeled IAV was measured by flow cytometry and expressed as mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) (n = 3). (b) The macrophages treated with 5 × 1010 QD649 particles for 30 min were stained with DAPI, and their phagocytic activity was determined by the Celigo cytometer. Representative images are shown (original magnification ×200, scale bar = 100 μm). The percentage of phagocytosis was identified as the proportion of macrophages (blue) engulfing QD649 (red) (n = 4). (c) The macrophages were cultured with biotin labeled-MDCK cells that had been infected with IAV at an MOI of 1 for 2 h, permeabilized, and then fixed for immunofluorescence staining. The cell mixtures were stained with anti-F4/80 antibody and Dylight-488 for detection of macrophages and biotin-labeled MDCK cells, respectively. The phagocytic activity was measured with the Celigo cytometer. Representative images are shown (original magnification ×200, scale bar = 100 μm). The percentage of phagocytosis was identified as the proportion of macrophages (red) engulfing MDCK cells (green) (n = 4). Arrows indicate macrophages that engulfed virus infected-MDCK cells (yellow).