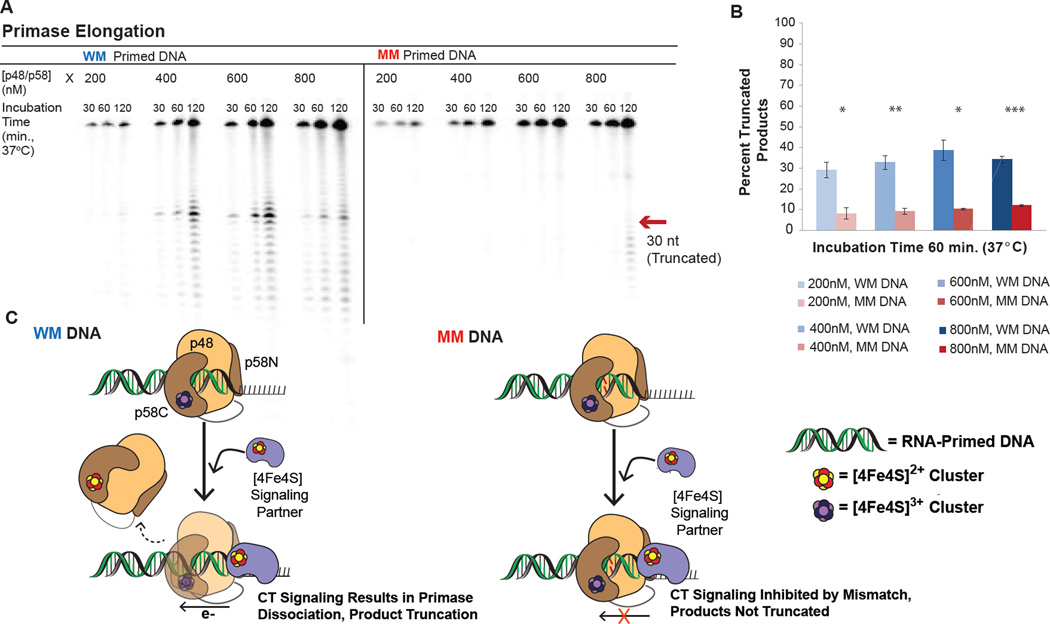
Figure 5. A Mismatch in the Nascent Primer Inhibits Primase Truncation.
A) Gel separation of elongation products on a 2’-OMe RNA- primed DNA substrate, when a well-matched (WM) or mismatched (MM) primer is synthesized by WT p48/p58. B) Average percent truncated products after 60 minutes of incubation at 37°C. WT primase synthesizes significantly more truncated products with a WM primer than a MM primer. C) Scheme illustrating the observed products in the mismatched primer elongation experiment. When p58C is in contact with the RNA/DNA primer, primase can signal another DNA-bound [4Fe4S] enzyme through a WM primer and dissociate from the template, truncating products. bottom left) DNA CT is inhibited with a MM primer, precluding redox signaling and primer truncation. Elongation assays were performed anaerobically, with 500nM primed DNA, 1 µM α-32P ATP, 200 µM CTP, 100 µM UTP, 200–800 nM p48/p58 in 50 mM Tris, pH 8.0, 3 mM MgCl2, at 37 °C. Quantifications shown are mean ± SD of n = 3 trials, * = 0.001<p<0.005, ** = 0.001<p<0.0005, *** = p<0.0005, student’s t-test.