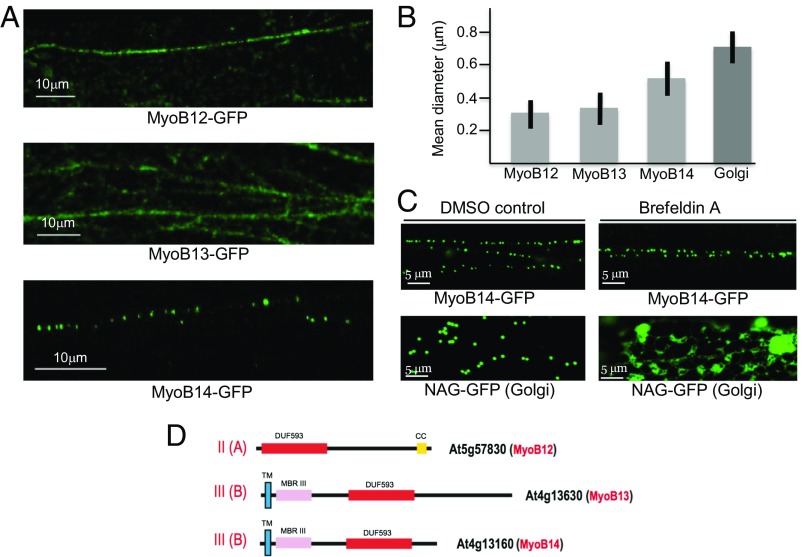
Fig. 2.
Analysis of MyoB12-GFP, MyoB13-GFP, and MyoB14-GFP localization and particle size in the leaf epidermal cells of transgenic Arabidopsis plants. (A) Distribution of the fluorescent bodies in linear vesicle-like arrays. (B) Mean diameters of the bodies associated with MyoB12-GFP, MyoB13-GFP, MyoB14-GFP, and Golgi stacks. (C) Distribution of the Golgi-specific marker NAG-GFP and MyoB14-GFP in leaf epidermal cells treated with DMSO (control) or BFA. (D) Domain architectures of the MyoB12, MyoB13, and MyoB14 that belong to subfamilies II(A) and III(B) as shown. CC, coiled coil; DUF593, a myosin-binding domain; MBRIII, predicted metal-binding domain III; TM, transmembrane α-helix.