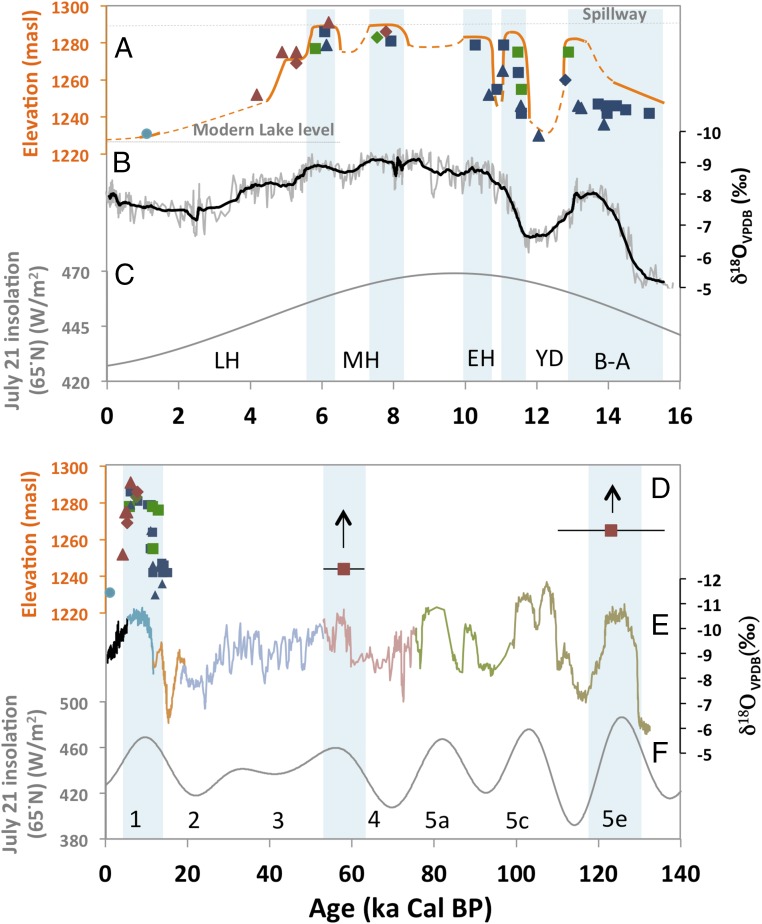
Fig. 2.
Lake level reconstruction. (A) Lake Dali level for the past 16 ka, lake sediments (square), alluvial deposits (triangle), and beach ridges (diamond) were dated using 14C from shell (blue), 14C from charcoal (green), and OSL (red). In situ shell layers deposited in the swash zone indicate shoreline proximity; shells found in secondary deposition within alluvial sediments indicate lake level was higher than the elevation the shells were eroded into (SI Materials and Methods; Tables S2–S4). The lowest section of the Jin Wall indicates an upper limit for lake level (turquoise circle). Dashed orange lines represent times when the magnitude of lake level change is uncertain. (B) Oxygen isotope composition from Dongge Cave (19). (C) North hemisphere summer (July 21) insolation at 65°N (2, 31). (D) Same as A for the past 140 ka. (E) Compiled oxygen isotope composition of the Chinese cave deposits (light blue is from Hulu Cave; all other colors are different stalagmites from Sanbao Cave) (2). (F) Same as C for the past 140 ka.