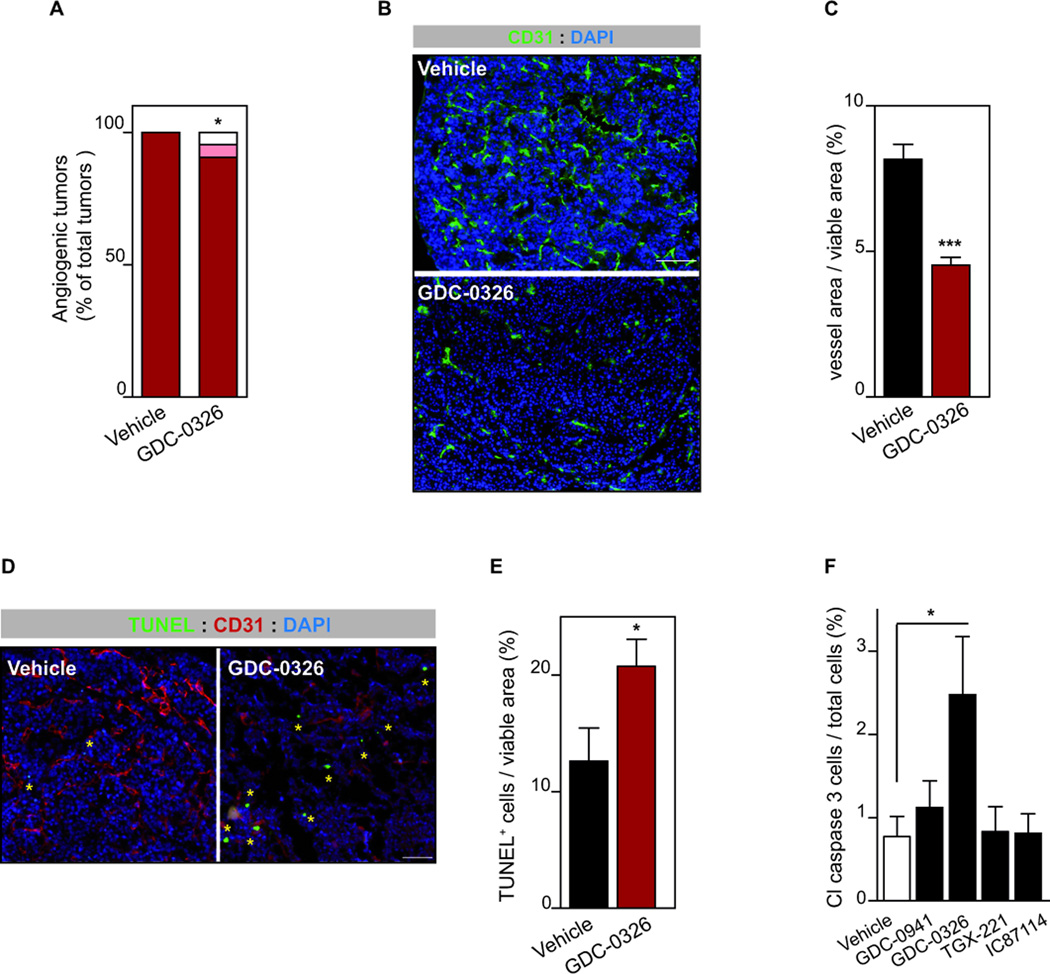
Figure 6. Inhibition of p110α results in cell intrinsic and extrinsic tumor effects.
A. Quantification of number of angiogenic “red” islet per mouse in vehicle (n=13) or GDC-0326 (n=7) for 2 weeks. B. CD31 and DAPI-stained sections of vehicle- or GDC-0326-treated RIP1-Tag2 tumors. Scale bar: 100 µm. C. The graph shows quantification of vessel area per tumor viable area of RIP1-Tag2 tumors treated with vehicle (n=8) or GDC-0326- (n=22). D. Sections of tumors stained for TUNEL (green), CD31 (red) and DAPI (blue). Yellow asterisk marks TUNEL positive cells Scale bar: 50 µm. E. Bar graphs show quantification of apoptotic cells per viable tumor area in RIP1-Tag2 tumors treated with vehicle (n=10) or GDC-0326- (n=14). E. Cell viability of βTC3 cells following 48 h in vitro treatment with vehicle, GDC-0941 (1 µM), GDC-0326 (1 µM), TGX-221 (0.5 µM) or IC87114 (5 µM), and analyzed by cleaved-caspase-3 immunoflorescence. Mean of eight independent experiments is shown. Error bars are standard error of the mean.