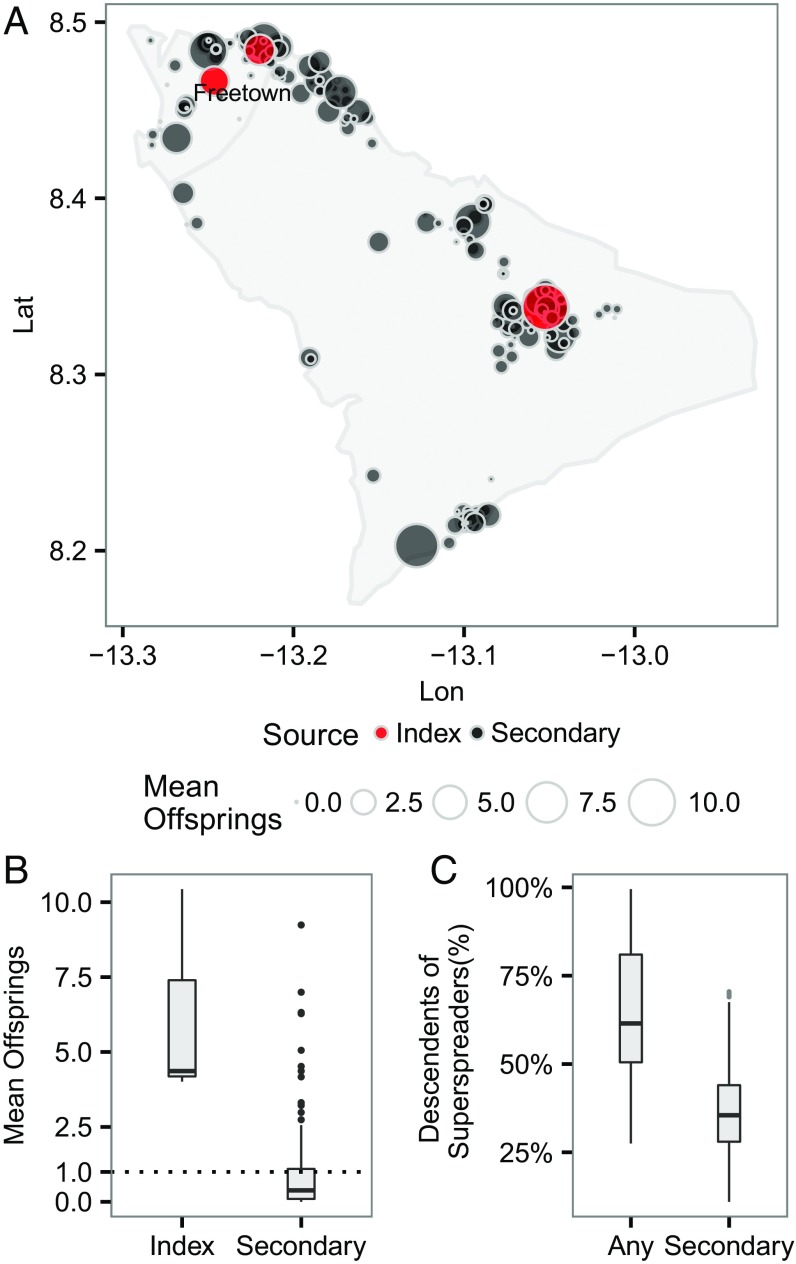
Fig. 2.
(A) Spatial distribution of mean number of offspring resulting from initial cases at the individual level. An infection is classified as an index case if it has a posterior probability of importation (i.e., not infected by any cases in the data) >0.5; otherwise, it is classified as a secondary case. Lat, latitude; Lon, longitude. (B) Distribution of mean number of offspring by different sources of infection. (C) Proportion of infected individuals who are direct and indirect descendants of the first five superspreaders (i.e., first five individuals with highest number of mean offspring; note that the choice of five is arbitrary here). “Any” includes superspreaders who were also the index cases (i.e., the roots of transmission trees).