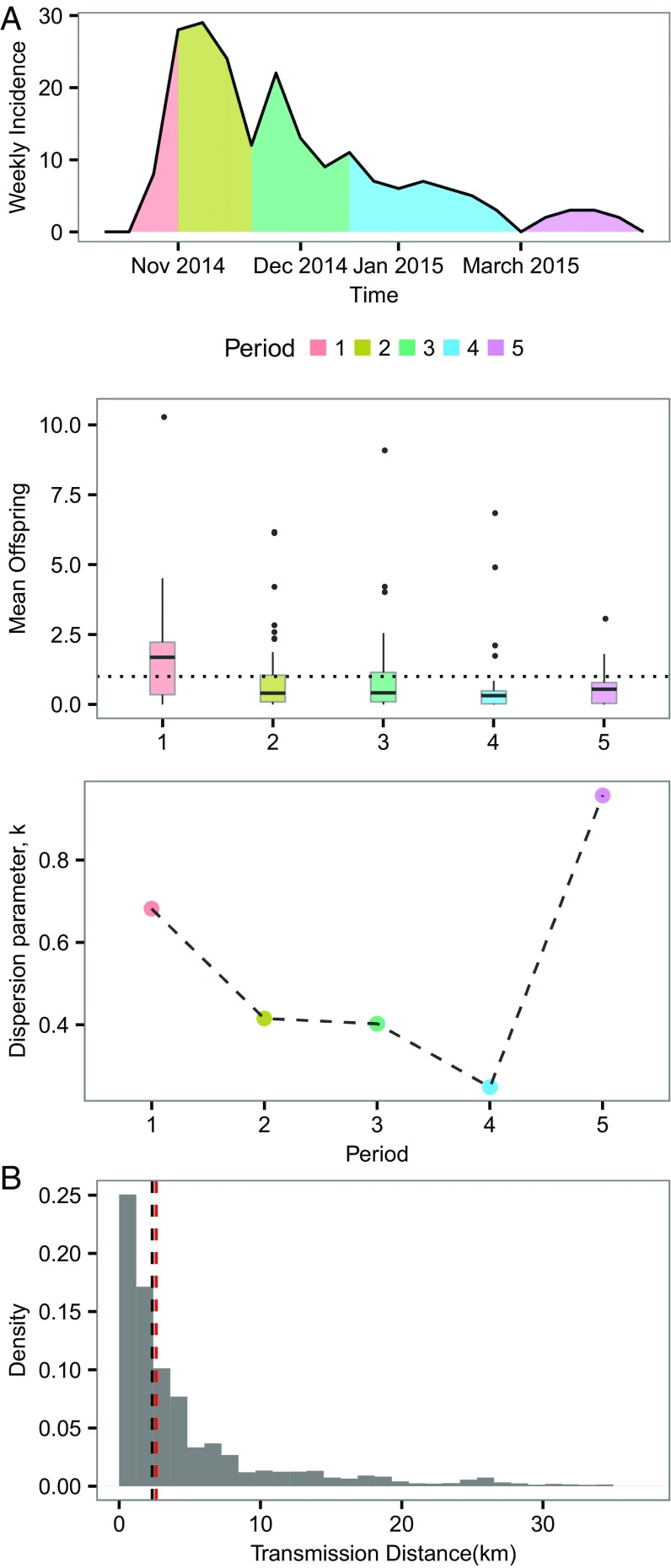
Fig. 3.
Spatial and temporal dependence of superspreading. (A) Reported weekly deaths and inferred mean offspring distributions and the corresponding empirical estimates of at different time periods. The whole time period is divided into five periodsthat is, period 1, from the time of first observation to the time of epidemic peak ; period 2, (, ); period 3, (, ); period 4, (, ); and period 5, from to the time of last observation. Such a dividing was used so that we could use the peak time as a reference point and ensure a similar number of cases in most intervals. (B) Distribution of distance of transmission for all infector–infected pairs. Black dotted line represents the median (2.51 km) of the distribution. Red dotted line represents the median (2.61 km) of the subdistribution in which the infectors are superspreaders (defined as those who has mean offspring more than five here).