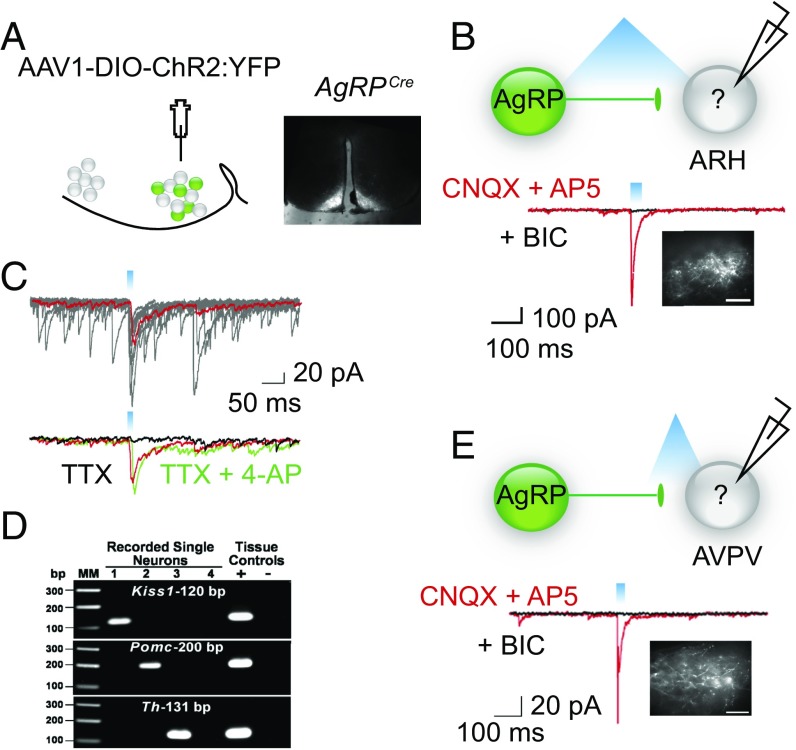
Fig. 2.
AgRP neurons can directly inhibit Kiss-expressing cells in the ARH and AVPV. (A) Map of the viral construct along with a diagram of the targeted injection site and confirmation of transduced neurons in the arcuate. (Scale bar, 300 μm.) (B) Trace recording from an undefined (nonfluorescent) cell in the ARH that exhibited a light-evoked IPSC in the presence of CNQX and AP5 (red trace) and was blocked by the addition of BIC (black trace). Cells were chosen based on proximity of the soma to fluorescent AgRP fibers. Inset demonstrates fluorescent AgRP fibers in the ARH. (Scale bars, 100 μm.) (C) The light-evoked fast IPSC response (red trace, average of 10 sweeps) was abolished in the presence of TTX (black trace) and rescued upon addition of the K+ channel blocker, 4-AP (green trace). (D) Analysis of cell lysates harvested from recorded cells via PCR detection of: Kiss1, Pomc, and Th cDNA. Reverse-transcribed cDNA from the hypothalamus was used as a positive control, whereas hypothalamic RNA was tested as the negative control. Water blanks were also included. (E) Blind recording of unidentified cell in the AVPV that demonstrated a light-evoked response. Note, for all recordings, fibers were stimulated with 330 μW of blue light at varying frequencies and pulse widths. Whole-cell, patch-clamp recordings were performed in the presence of CNQX (10 μM) and AP5 (50 μM) and the evoked responses were blocked by BIC (30 μM). (Scale bar, 100 μm.)